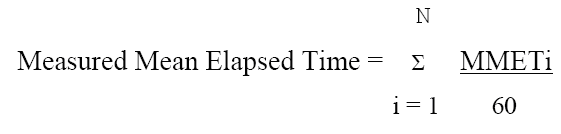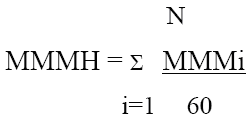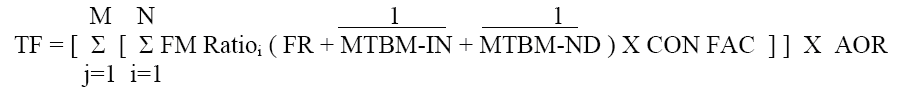For the purposes of this specification, the following terms apply:
A code that represents a functional or hardware generation breakdown/disassembly sequence of system/equipment hardware including
SE, training equipment, and installation (connecting) hardware. For additional information on assignment of LCN, refer to
the GEIA-HB-0007.
A five-character code assigned by the DLIS to the design control activity or actual manufacturer of an item as contained in
the Cataloging Handbook H4/H8 Series. Assistance in finding CAGE codes may be found at http://www.dlis.dla.mil/cage_welcome.asp
A designation assigned to a particular drawing or document by the authoritive source for identification purposes. The document
id may include numbers, letters, and dashes.
A set of operationally related tasks within a given Job, e.g., driving, item servicing, communicating, and operator maintenance.
An assigned code that is associated with a specific duty.
A single-position code to indicate whether or not the procedural subtask is a task element.
Task Element: The smallest logically and reasonably
definable unit of behavior required to complete a task or subtask. - E
Not a Task Element - Blank
A code that uniquely identifies the system/equipment end item. This code will be assigned by the requiring authority. It will
remain constant throughout the item's life cycle (e.g., TOW, PATRIOT, Tomahawk, Sparrow, and ALCM).
The combination of all human performance required for operation and maintenance of one personnel position in a system (e.g.,
driver).
An assigned code that is associated with a specific job.
A code that represents a functional or hardware generation breakdown/disassembly sequence of system/equipment hardware including
SE, training equipment, and installation (connecting) hardware. For additional information on assignment of LCN, refer to
the GEIA-HB-0007.
An identifying noun with an appropriate adjective modifier identifying the LCN item. When using the modified classical LCN
assignment method, then "REPAIR PARTS" is used to identify an LCN representing more than one reference number and CAGE combination.
The number of operational units (e.g., rounds, miles, hours) between preventive maintenance derived as an outcome of the RCM
analysis.
A code that categorizes a maintenance task as corrective, a preventive based on calendar time, or a preventive based on a
rate of use.
The title of a maintenance procedure.
The number of items used to perform the task. For tasks where the items are not used for every occurrence of the task, the
quantity per task is the expected average number of items per task.
A code that identifies the breakdown sequence of an assembly, below the standard numbering system (SNS) level, to which maintenance
and descriptive information applies. This is a constituent of the S1000D Data Module Code. It includes codes 00 to 99; then
A1 to A9, and so on. Omit the characters I and O .
A code used to identify the type of information in a data module. Refer to the S1000D Standard at S1000D.org.
A code used to identify different data modules that are applicable to the same subject and type of data. Refer to the S1000D
Standard at S1000D.org.
The mean man-minutes required for each person identified to perform a step within a task expressed in minutes and tenths.
The mean minute elapsed time required for each subtask, expressed in minutes and tenths, regardless of the number of personnel
working simultaneously. This does not include logistic delay time.
A three-position code to indicate sequence of the procedural step as a subtask. Subtask numbers shall begin with 001 through
999, and are assigned to each sequential subtask required to perform a given task. A subtask is an activity (perception, decisions,
and responses) that fulfills a portion of the immediate purpose within a task.
A three-position code identifying each person required to perform the subtask (codes "A" through "999"). Within a task, a
given Person ID relates to a specific "Job" and a specific Skill Specialty Code.
An access point shall be identified by a code consisting of up to ten characters. The access code will clearly indicate points
of access required for maintenance purposes.
Typical access points include: doors, panels, floor and ceiling panels, hatches and
fairings. This equates to S1000D ACCESS.
A code that identifies a work area zone. Zones shall be identified by a code consisting of up to ten characters. This equates
to S1000D ZONE.
A data chain of six separate data subfields that uniquely identify each operator/maintenance task associated with particular
items under analysis. The first five subfields provide information relative to the performance of the task itself. The sixth
subfield is a task sequence code provided to differentiate tasks with identical entries in the first five subfields.
Indicator that special considerations must be taken into account during analysis of the task.
Task Condition A TM/Technical Order use not feasible (inadequate lighting, space constraints, or time constraints) Y or N
Task Condition B TMDE/ATE/BIT/BITE required Y or N
Task Condition C Special tools required Y or N
A task is a composite of related activities (perceptions, decisions, and responses) performed for an immediate purpose, written
in operator/ maintainer language. Task identification requires a brief narrative entry consisting of: (a) an action verb that
identifies what is to be accomplished in the task or subtask; (b) an object that identifies what is to be acted upon in the
task/subtask; and, (c) qualifying phrases needed todistinguish the task from related or similar tasks. Recommended action
verbs to be used in preparing task or subtask identifications may be drawn from the following list. Some specialized verbs,
not listed below, may be needed for a particular system/equipment.
Many verbs are synonymous. The preparing activity should select one verb that appears closest to the intended meaning for
the system/equipment under analysis, and use that verb consistently throughout the analysis. Some verbs are more appropriate
for writing statements of tasks, while some verbs are exclusive to subtask elements.
Access. (a) To gain visibility of or the ability to manipulate. (b) To cause to be
displayed, as with a computer menu.
Accomplish. To do, carry out, or bring about; to reach an objective.
Achieve. To carry out successfully.
Acknowledge. To make known the receipt or existence of.
Actuate. To put into mechanical motion or action; to move to action.
Adjust. (a) To bring to a specified position or state. (b) To bring to a more satisfactory
state; to manipulate controls, levers, linkages, etc., to return equipment from an out of
tolerance condition to an in tolerance condition.
Administer. To manage or supervise the execution, use, or conduct of.
Advance. To move forward; to move ahead.
Advise. To give information or notice to.
Alert. To warn; to call to a state of readiness or watchfulness; to notify (a person) of an
impending action.
Align. To bring into line; to line up; to bring into precise adjustment, correct relative
position; or coincidence.
Allocate. To apportion for a specific purpose or to particular persons or things.
Allow. (a) To permit; to give opportunity to. (b) To allot or provide for. (c) To carry out
a procedure.
Analyze. To examine and interpret information.
Annotate. To append explanatory information to a text or graphic summary of information.
Announce. To make known.
Apply. (a) To lay or spread on. (b) To energize.
Approve. To give offical sanction.
Archive. To make an archival copy of.
Arrange. To group according to quality, value, or other characteristics; to put in proper
order.
Assault. Close combat phase of an attack.
Assemble. To fit and secure together the several parts of; to make or form by combining
parts.
Assess. To determine the importance, size, or value of; to evaluate.
Assign. To apportion to for a specific purpose or to particular persons or things; to
appoint to a duty.
Assist. To give support or help; to aid.
Attach. To join or fasten to.
Authenticate. To prove or serve to prove the authenticity of.
Balance. To equalize in weight, height, number, or proportion.
Breach. (a) To break through. (b) To secure passage through.
Brief. To give final precise instructions; to coach thoroughly in advance; to give
essential information to.
Bypass. Maneuver around an obstacle, position, or enemy force to maintain momentum
of advance.
Calculate. To determine by arithmetic processes.
Calibrate. To determine accuracy, deviation, or variation by special measurement or by
comparison with a standard.
Camouflage. To conceal or disguise.
Cancel. To cause not to occur, as in canceling a command. Categorize. To put into
categories or in general classes.
Center. (a) To adjust so that axes coincide. (b) To place in the middle of.
Check. (a) To confirm or establish that a proper condition exists; to ascertain that a given
operation produces a specified result; to examine for satisfactory accuracy, safety, or
performance; to confirm or determine measurements by use of visual or mechanical
means. (b) To perform a critical visual observation or check for specific conditions; to
test the condition of.
Chock. To place a blocking device adjacent to, in front of, or behind a wheel to keep it from moving.
Choke. To enrich the fuel mixture of a motor by partially shutting off the air intake of
the carburetor.
Choose. To select after consideration.
Chunk. To cause the association of several entities. Classify. To put into categories or
general classes.
Clean. To wash, scrub, or apply solvents to; remove dirt, corrosion, or grease.
Clear. (a) To move people/objects away from. (b) To open the throttle of an idling
engine to free it from carbon.
Close. (a) To block against entry or passage; to turn, push, or pull in the direction in that
the flow is impeded. (b) To set a circuit breaker into the position allowing current to
flow through.
Collect. To bring together into one body or place; to accumulate. Command. To direct
authoritatively.
Communicate. (a) To exchange information. (b) To make known.
Compare. To examine the character or qualities of two or more items; to discover
resemblances or differences.
Complete. (a) To bring to an end. (b) To supply missing or needed information, normally in a prescribed format.
Comply. To conform with directions or rules; to accept as authority; to obey.
Compute. To determine by arithmetic process.
Condense. To make denser, more brief, or more compact.
Connect. (a) To bring or fit together so as to form a unit; to couple keyed or matched
equipment items. (b) To attach or mate (an electrical device) to a service outlet.
Construct. (a) To make or form by combining parts; to fit and secure together the several
parts of. (b) To assemble information elements or entities in a specified fashion.
Control. To exercise restraining or directing influence over; to fix or adjust the time,
amount, or rate of.
Coordinate. To bring into a common action, movement, or condition.
Correct. To make or set right, to alter or adjust so as to bring to some standard or
required condition.
Correlate. To establish a mutual or reciprocal relation between.
Cover. To protect or shelter by placing something over or around.
Create. To cause or come into being, normally based on some established criterion.
Debug. To detect and remedy an inadequacy in software.
Decide. To arrive at a solution.
De-energize. To take energy from.
Define. (a) To determine or identify the essential qualities or meaning. (b) To fix or
mark the limits of.
Deflate. To release air or gas from.
Delete. To remove from association with or cause no longer to exist.
Deliver. (a) To hand over. (b) To send to an intended target or destination.
Demonstrate. To show clearly.
Depart. To go away; to leave.
Depressurize. To release gas or fluid pressure from.
Derive. To infer or deduce.
Describe. To represent or give an account of in words.
Destroy. To ruin, demolish, or put out of existence; to make unfit for further use.
Detect. To discover or determine the existence, presence, or fact of.
Determine. (a) To obtain definite and first-hand knowledge of, to confirm, or establish
that a proper condition exists. (b) To investigate and decide to discover by study or experience.
Develop. To set forth or make clear by degrees or in detail.
Diagnose. To recognize and identify the cause or nature of a condition, situation, or
problem by examination or analysis.
Disassemble. To take to pieces; to take apart to the level of the next smaller unit or down
to all removable parts.
Disconnect. (a) To sever the connection between; to separate keyed or matched
equipment parts. (b) To detach or separate (an electrical device) from a service outlet.
Discriminate. To distinguish or differentiate by discerning or exposing differences.
Disengage. To release or detach interlocking parts; to unfasten; to set free from an
inactive or fixed position.
Dismantle. To take apart.
Dismount. (a) To get. (b) To take off.
Displace. To leave one position and take another.
Display. To cause a visual image to be presented on some medium.
Dispose of. To get rid of.
Disseminate. To distribute or disperse to more than one.
Distinguish. To perceive a difference in.
Distribute. To deliver.
Drain. To draw off (liquid) gradually or completely.
Draw. To produce a likeness or representation of.
Drive. To direct the course and motions of a vehicle.
Edit. To correct errors of grammar, syntax, and content in text material.
Effect. To cause the desired result or outcome.
Egress. To go out.
Elaborate. To provide more detail regarding.
Elevate. To lift up; to raise.
Eliminate. To expel; to ignore or set aside as unimportant.
Emplace. To put into position.
Employ. To put into action or service; to carry out a purpose or action by means of; to
avail oneself of.
Energize. To impart energy to.
Enforce. To compel or constrain.
Engage. (a) To cause to interlock or mesh. (b) To enter into conflict.
Ensure. (a) To make sure or certain. (b) To guarantee.
Enter. (a) To go or come in. (b) To put on record. (c) To put in information or data.
Erect. To put up by fitting together.
Establish. To set on a firm basis.
Estimate. To judge or determine roughly the size, extent, or nature of.
Evacuate. To move from an area.
Evade. To avoid.
Evaluate. To determine the importance, size, or nature of; to appraise; to give a value or
appraisal to on the basis of collected data.
Exchange. To part with or substitute.
Execute. To carry out fully.
Explain. To make something plain and understandable.
Express. To represent in words; to state.
Extract. To draw forth; to pull out forcibly.
Fill out. To enter information on a form.
Find. (a) To discover or determine by search; to indicate the place, site, or limits of. (b)
To discover by study or experiment; to investigate and decide.
Fire. To launch a missile or shoot a gun.
Format. To produce in a specified form or style.
Fuel. To provide with fuel.
Harden. To protect.
Hold. To have or keep in the grasp.
Hypothesize. To develop a prediction or speculation, of some degree of uncertainty,
based on incomplete factual information or theory.
Identify. (a) To establish the identity of. (b) To determine the
classification of.
Illustrate. To make clear or clarify.
Implement. To place into effect.
Indicate. To point out.
Inform. To make known to; to give notice or report the occurrence of.
Initialize. To place in an initial or beginning condition.
Input. To enter information into a computer or data system.
Insert. To put or thrust in, into, or through.
Inspect. To perform a critical visual observation or check for specific conditions; to test
the condition of.
Install. (a) To perform operations necessary to properly fit an equipment unit into the
next larger assembly or system. (b) To place or attach.
Instruct. To provide with authoritative information or advice.
Integrate. To bring together information from two or more different sources for the
purpose of combining analysis or presentation.
Intercept. To stop or interrupt the progress or course of.
Interchange. To remove one item from an assembly and install a like item in the same
assembly.
Interpret. (a) To conceive in the light of individual belief, judgment, or circumstance. (b)
To explain the meaning of.
Investigate. To observe or study by close examination and systematic inquiry.
Isolate. To use test equipment to identify or select a source of trouble.
Issue. To put forth or distribute.
Lead. To go at the head.
Lift. To move or cause to be moved from a lower to a higher position; to elevate.
List. To enumerate; to write the names of a group of items together.
Listen. To hear something with thoughtful attention.
Load. To place in or on; to place cargo or components on an airplane or other vehicle.
Locate. (a) To find, determine, or indicate the place, site, or limits of. (b) To set or
establish in a particular spot; to station.
Log. (a) To record for purposes of keeping records. (b) To gain access to a computer
system or terminate interaction with a computer system.
Lubricate. To put lubricant on specified locations.
Maintain. (a) To hold or keep in a particular state or condition, especially in a state of
efficiency or validity. (b) To sustain or keep up.
Manage. To handle or direct with a degree of skill.
Maneuver. To make a series of changes in direction and position for a specified purpose.
Measure. To determine the dimensions, capacity, or amount by use of standard
instruments or utensils.
Modify. To alter or change somewhat the form or qualities of.
Monitor. (a) Visually to take note of or to pay attention to in order to check on action or
change. (b) To attend to displays continually or periodically to determine equipment
condition or operating status. Mount. To attach to a support.
Move. To change the location or position of.
Name. To identify by name.
Navigate. To operate and control course of.
Neutralize. To destroy the effectiveness of; to nullify.
Notify. To make known to; to give notice or report the occurrence of.
Observe. (a) To conform one's actions or practice to. (b) To take note of visually; to pay
attention to.
Obtain. (a) To get or find out by observation or special procedures. (b) To gain or attain.
Occupy. (a) To reside. (b) To control.
Open. (a) To move from closed position; to make available for passage by turning in an
appropriate direction. (b) To make available for entry or passage by turning back,
removing, or clearing away.
Operate. To control equipment in order to accomplish a specific purpose.
Organize. To arrange elements into a whole of interdependent parts; to form into a
coherent unity; to integrate.
Orient. (a) To acquaint with the existing situation or environment. (b) To set or arrange
in a determinate position.
Originate. To give rise to, to set going, to begin.
Pack. To gather.
Park. To bring a vehicle to a stop and leave it standing for a time in a specified area.
Perform. To do, carry out, or bring about; to reach an objective.
Place. To put or set in a desired location or position.
Plan. To devise or project the achievement of.
Plot. To mark or note on or as if on a map or chart; to locate by means of coordinates.
Police. (a) To make clean. (b) To put in order.
Position. To put or set in a given place. Post. To station at a given place.
Prepare. To make ready; to arrange things in readiness.
Prescribe. To lay down as a guide, direction, or rule of action; to specify with authority.
Press. To act upon through thrusting force exerted in contact.
Pressurize. To apply pressure within by filling with gas or liquid.
Prevent. To keep from happening or existing.
Prioritize. To arrange or list in order of priority or importance.
Process. To submit to a series of actions or operations leading to a particular end.
Procure. (a) To bring about. (b) To acquire or obtain.
Produce. To cause to come into being or visibility.
Program. To work out a plan or procedure or a sequence of operations to be performed.
Protect. To shield from damage, injury, or destruction.
Provide. To supply what is needed, to equip.
Publish. To produce for distribution.
Pull. To exert force upon an object so as to cause motion toward the force.
Pump. (a) Raise or lower by operating a device that raises, transfers, or compresses
fluids by suction, pressure or both. (b) To move up and down or in and out as if with a
pump handle.
fluids by suction, pressure or both. (b) To move up and down or in and out as if with a
pump handle.
Purge. (a) To expel unwanted fluids from. (b) To cause to be eliminated or disassociated
from.
Push. (a) To press against with force so as to cause motion away from the force. (b) To
move away or ahead by steady pressure.
Qualify. To declare competent or adequate.
Queue. To cause to be placed in a queue or ordered sequence of similar processes.
Raise. To move or cause to be moved from a lower to a higher position; to elevate.
Reach. To arrive at.
React. To respond.
Read. To derive information from written material.
Recall. To bring forth information from memory. Receive. To come into possession of;
to get.
Recognize. To perceive to be something previously known or designated. Recommend.
To consel and advise that something be done.
Reconnoiter. To obtain information by visual observation, or other detection methods.
Record. To set down in writing. Recover. To get back; to regain. Redistribute. To
reallocate.
Refuel. To put fuel into the tanks of a vehicle again.
Release. (a) To set free from an inactive or fixed position; to unfasten or detach
interlocking parts. (b) To let go of. (c) To set free from restraint or confinement.
Relocate. To change the place or position of.
Remove. (a) To perform operations necessary to take an equipment unit out of the next
larger assembly or system. (b) To take off or eliminate. (c) To take or move away. (d) To
take off devices for closing off the end of a tube.
Reorganize. To organize again.
Repair. To restore damaged, wornout, or malfunctioning equipment to a serviceable,
usable, or operable condition.
Repeat. To make, do, or perform again.
Replace. (a) To restore to a former place of position. (b) To substitute serviceable
equipment for malfunctioning, wornout, or damaged equipment.
Replenish. To fill again.
Report. (a) To describe as being in a specified state. (b) To make known to; to give
notice or report the occurrence of.
Represent. To cause information to be conveyed in a fashion different from the original.
Request. To ask for.
Reset. To put back into a desired position, adjustment, or condition.
Resolve. To eliminate discrepancies from two or more sources of information.
Respond. To react.
Resume. To begin again.
Retrieve. To cause to be removed from storage or other unavailable state and made
accessible.
Review. To examine again; to go over or examine critically or deliberately.
Rotate. To cause to revolve about an axis or center.
Route. To send by a selected course of travel; to divert in a specified direction.
Run. To cause a computer program to be executed by a computer.
Save. To cause to be stored or placed in an accessible location.
Scan. To make a wide, sweeping search of; to look through or over hastily.
Schedule. To appoint, assign, or designate for a fixed future time; to make a timetable of.
Search. To examine a context to determine the presence of a particular entity or type of
entity.
Secure. To make fast or safe.
Select. To take by preference or fitness from a number or group; to pick out, to choose.
Send. To dispatch by means of communication.
Service. To perform such operations as cleanup, lubrication, and replenishment to
prepare for use.
Set. (a) To put a switch, pointer, or knob into a given position; to put equipment into a
given adjustment, condition or mode. (b) To put or place in a desired orientation,
condition, or location.
Set up. To prepare or make ready for use.
Show. To point out or explain.
Shut down. To perform operations necessary to cause equipment to cease or suspend
operation.
Sight. (a) To look at through or as if through a sight. (b) To aim by means of sights.
Signal. To notify or communicate by signals (i.e., a prearranged sign, notice or symbol
conveying a command, warning, direction or other message).
Solve. To find a solution for.
Specify. To name or state explicitly or in detail.
Squeeze. To force or thrust together by compression.
Start. To perform actions necessary to set into operation; to set going; to begin.
State. To express the particulars of in words.
Stay. To remain; to continue in a place.
Steer. To direct the course of.
Stop. To perform actions necessary to cause equipment to cease or suspend operation.
Store. To cause to be placed in an accessible location.
Stow. To deposit or leave in a specified place for future use.
Strike. To deliver or aim a blow or thrust; to hit.
Submit. To make available; to offer.
Summarize. To tell in or reduce to a summary.
Supervise. To oversee; to have or exercise the charge of.
Support. To assist; help.
Sweep. To clean.
Synthesize. To combine or produce by synthesis.
Take. (a) To get into or carry in one's hands or one's possession. (b) To get or find out by
observation or special procedures.
Tap. To strike lightly.
Task. To assign responsibility.
Tell. To express in words.
Test. To perform specified operations to verify operational readiness of a component,
subcomponent, system, or subsystem.
Tighten. (a) To perform necessary operations to fix more firmly in place. (b) To apply a
specified amount of force to produce a rotation or twisting motion to fix more firmly in
place.
Trace. To follow or study out in detail or step by step.
Transfer. To cause an entity to change location or association with other entities.
Transmit. (a) To convey or cause to pass from one place to another. (b) To send out a
signal by radio waves or wire.
Transport. (a) To convey or cause to pass from one place to another. (b) To carry by
hand or in vehicle or hoist, or in a container, etc.
Traverse. To move from side to side.
Treat. To care for medically.
Troubleshoot. To localize and isolate the source of a malfunction or break down.
Turn. To cause to revolve about an axis or center.
Type. To enter information into a device by means of a keyboard.
Unload. To take off.
Update. To replace older, possibly invalid, information with more current information.
Use. To put into action or service; to avail oneself of; to carry out a purpose or action by
means of.
Utilize. To put into action or service; to avail oneself of; to carry out a purpose or action
by means of.
Validate. To ascertain the correctness of, using an independent source of information.
Verify. (a) To confirm or establish that a proper condition exists. (b) To establish the
truth or accuracy of.
Visualize. To create a mental picture or concept of.
Wait. To suspend activity in a sequence of activities until a given condition occurs or a
set time has elapsed.
Write. To inscribe words on a surface.
Zero. To bring to a desired level or null position.
An assigned identification to a task that is unique within the Product (End Item).
A very brief description of peculiar or unusual maintenance requirements associated with a specific task. These statements
are included in section IV of the maintenance allocation chart (MAC).
A code used to uniquely identify a specific remark. Once associated with a remark, a code may not be associated with any other
remark, regardless of the LCN and Task Code. Once assigned, the same code shall be used to identify subsequent occurrences
of that remark, regardless of the LCN and Task Code.
A four position number that indicates the sequence of a procedural step for a task. The number begins with 1 and ends with
9999.
The Special Requirements narrative is associated with Task/Subtask Associated Narrative Code “C”. and contains details of
any special general requirements applicable to the item during maintenance and handling, eg., safety precautions and special
facilities and equipment etc.
The Warning Information narrative is associated with Task/Subtask Associated Narrative Code “D”. It is narrative information
which denotes possible hazards, which may cause loss of life, physical injury or ill health during the performance of tasks/subtasks.
This equates to AECMA 1000D WARNING INFORMATION.
The Caution Information narrative is associated with Task/Subtask Associated Narrative Code “E”. This Narrative information
denotes the possibility of damage to materiel during the performance of tasks/subtasks. This equates to AECMA 1000D CAUTION
INFORMATION.
The Note information narrative is associated with Task/Subtask Associated Narrative Code “F”. This Narrative is Supplementary
task/subtask-related narrative information, not covered in Warning Information or Caution Information. This equates to AECMA
1000D NOTE INFORMATION.
The identification code assigned to a specific manual.
A code that indicates the configuration of a system/equipment on which the item under analysis is used. The UOC represents
only one configuration/model of equipment. It is a one, two, or three-character alphanumeric entry with guidance for UOC assignment
provided by the requiring authority. When an item is applicable to multiple equipment configurations, multiple UOCs representing
each configuration are assigned to the item.
A code that identifies a work area zone. Zones shall be identified by a code consisting of up to ten characters. This equates
to S1000D ZONE.
NOTE These terms are not part of the released specification.