| DEX: (D002) fault_states — Faults related to products | Date: 2007/09/14 16:11:29 Revision: 1.28 |
This section is a detailed description on how to implement a typical fault state analysis result in PLCS, using defined PLCS capabilities and PLCS reference data.
This implementation may be further tailored by specific parties, firstly by extending the reference data library, and secondly by introducing new relationships between entities available in the schema for the Fault states DEX, which are not used in this basic implementation of the DEX.
The implementation details are organized in accordance with the section 'Fault state analysis result - Information Content' above.
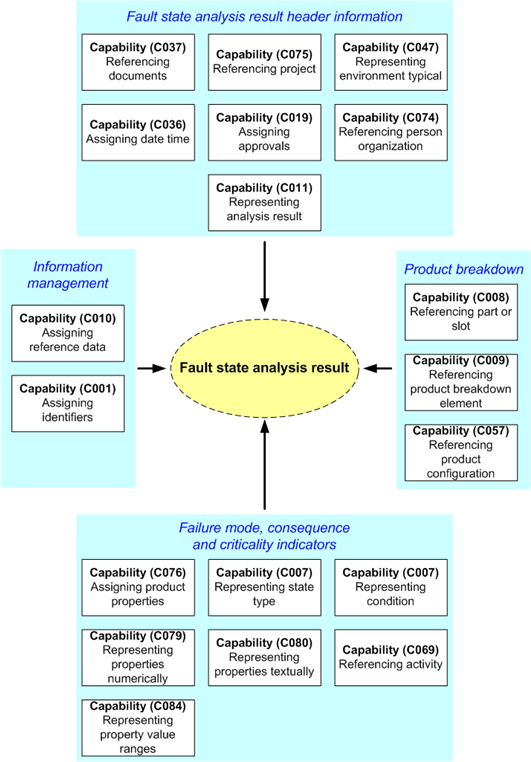
An overview of the capabilities used by this DEX is shown in figure 1 below.

A fault state analysis result is an actual product and is therefore represented as a
Product_as_realized
as described in the C011: representing_analysis_result capability.
The actual fault state analysis result
(Product_as_realized)
is a realization of a
Part
representing all editions of the fault state analysis result. The
Part
should be classified as [Fault_state_analysis_result]![]() Error RDL1: The class Fault_state_analysis_result does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Fault_state_analysis_result does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and the
Product_as_realized
should be classified as [Revision]![]() Error RDL1: The class Revision does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Revision does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.

The representation of the general administrative and context information of a fault state analysis result, is based on the constructs described within the "Representing context information" section of the C011: representing_analysis_result capability, along with some additional reference data.
The general administrative information is represented as follows:
NOTE For more details on how to represent the identification of an analysis result see the "Identification" section of the C011: representing_analysis_result capability.
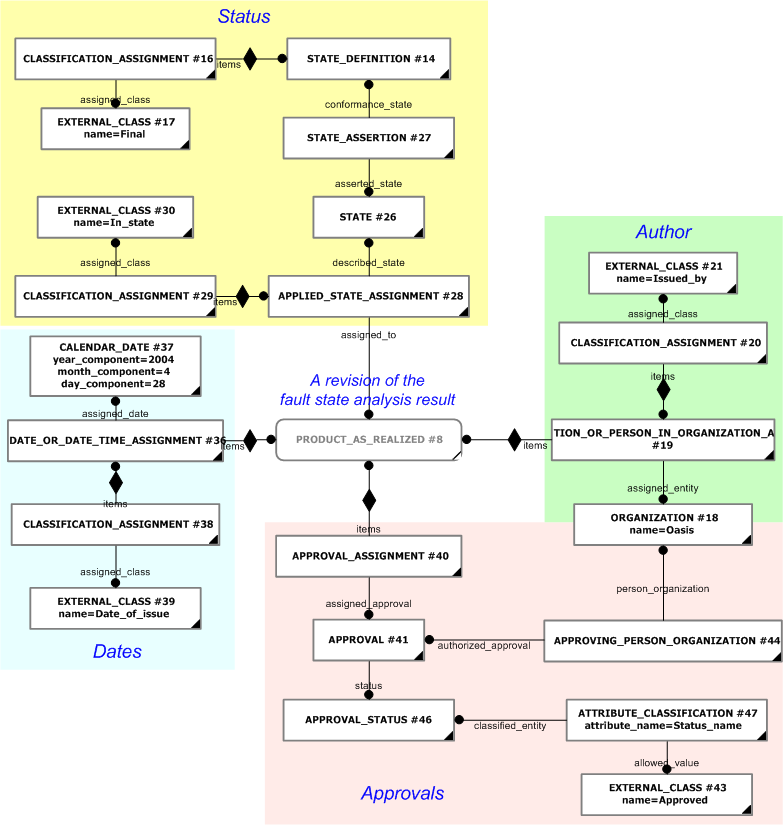
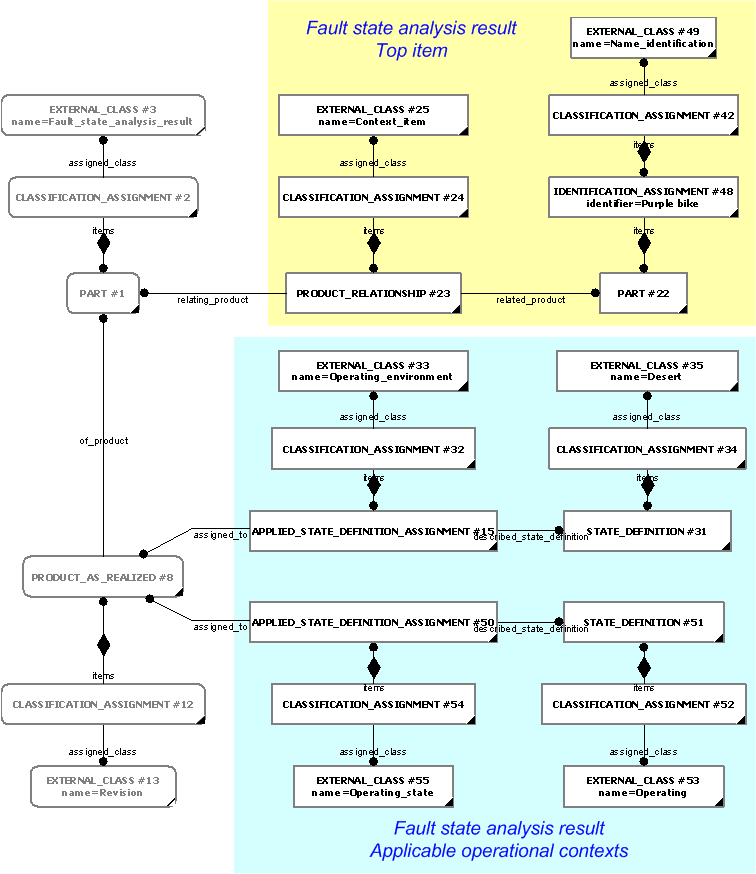
The instance diagrams in figure 5 and figure 6 illustrates some of some of the general administrative information given in figure 1.
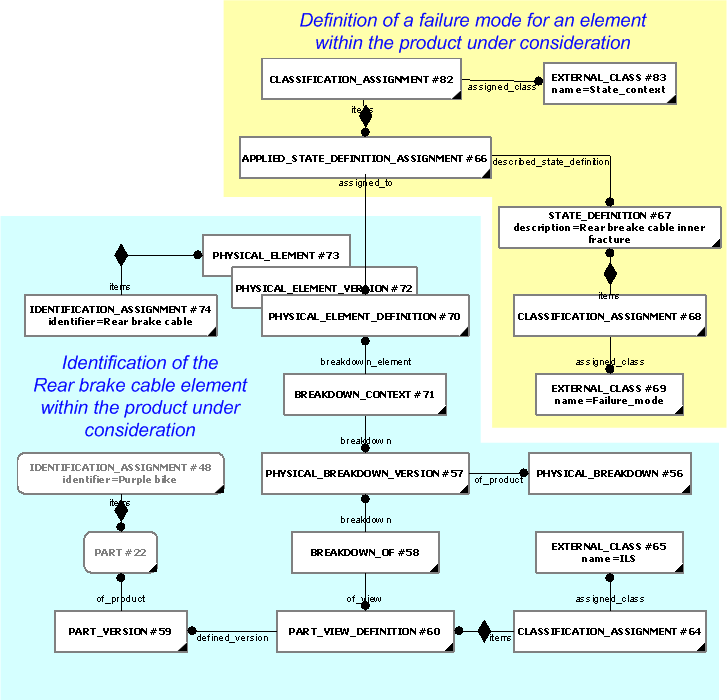
The representation of the detail data section is based on the usage guidance provided in the "Representing content information" section in the C011: representing_analysis_result capability.
The detail data section of a fault state analysis result identifies two different breakdown/assembly structures of the product under consideration, namely:
Each record in an fault state analysis result is based on a failure mode being assigned to a Physical_element or a Part, within the Physical breakdown or Assembly structure of the product under consideration.
Failure mode description and characterization
Classification
Each failure mode is represented as a
State_definition being assigned
to a
Physical_element or a
Part
using
Applied_state_definition_assignment.
The Part
or the
Physical_element being
assigned with a failure mode, may be referenced
in several different ways
as described in the referencing_part_or_slot![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_part_or_slot not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_part_or_slot not in dex_index.xml
,
referencing_product_breakdown_element![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_product_breakdown_element not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_product_breakdown_element not in dex_index.xml
and the referencing_product_configuration![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_product_configuration not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_product_configuration not in dex_index.xml
capabilities.
NOTE
The respective breakdown element/part in the breakdown/assembly is referenced by its identifier.
Each identification should be classified. Typical values are [Part_code]![]() Error RDL1: The class Part_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Part_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
,
[LCN_code]![]() Error RDL1: The class LCN_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class LCN_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
, [Name_identification]![]() Error RDL1: The class Name_identification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Name_identification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The State_definition
should be classified as [FailureMode]![]() Error RDL1: The class FailureMode does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class FailureMode does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and the
Applied_state_definition_assignment
should be classified as [StateContext]![]() Error RDL1: The class StateContext does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class StateContext does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Identification
Each State_definition may have
a unique identification using the C001: assigning_identifiers capability.
The Identification_assignment
should be classified as [FailureModeIdentification]![]() Error RDL1: The class FailureModeIdentification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class FailureModeIdentification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Description
The State_definition. description attribute should contain a textual description of the failure mode.
Cause
The cause of a failure mode occurring should be represented as an Activity being assigned to the Applied_state_definition_assignment representing the association between the failure mode and the product under consideration.
The Activity representing the cause of a failure mode occurring may be classified. Typical values includes:
The Applied_activity_assignment
should be classified as [CauseEffect]![]() Error RDL1: The class CauseEffect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class CauseEffect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
NOTE There should be one Applied_state_definition_assignment for each cause of a failure mode.
Predictability
Predictability represented by qualifiers are represented as
Classification_assignment
of the
Applied_state_definition_assignment
representing the association between the failure mode state and the product under consideration.
Typical values includes [Predictable]![]() Error RDL1: The class Predictable does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Predictable does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and [Unpredictable]![]() Error RDL1: The class Unpredictable does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Unpredictable does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Predictability represented as calculated values
are represented as an Assigned_property
as described in the C076: assigning_product_properties
and C079: representing_properties_numerically capabilities. The
Assigned_property
is assigned to the
Applied_state_definition_assignment
representing the association between the failure mode state and the product under consideration.
The Assigned_property
should be classified as [Predictability]![]() Error RDL1: The class Predictability does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Predictability does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
, and the
Unit
should be classified in accordance with the
method used to calculate the predictability. Typical values include
[P_F_interval]![]() Error RDL1: The class P_F_interval does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class P_F_interval does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and [Weibull_beta_parameter]![]() Error RDL1: The class Weibull_beta_parameter does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Weibull_beta_parameter does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Detection method
Detection methods are represented as
Activity_methods using the
referencing_activity![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_activity not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_activity not in dex_index.xml
capability.
The association between the
State_definition representing the
failure mode state and the Activity_method
representing the detection method is established via a
Applied_state_definition_assignment.
The Applied_state_definition_assignment
should be classified as [Detection_method]![]() Error RDL1: The class Detection_method does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Detection_method does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
, and the
Activity_method should be
classified to reflect the class of detection method being defined. Typical values includes:
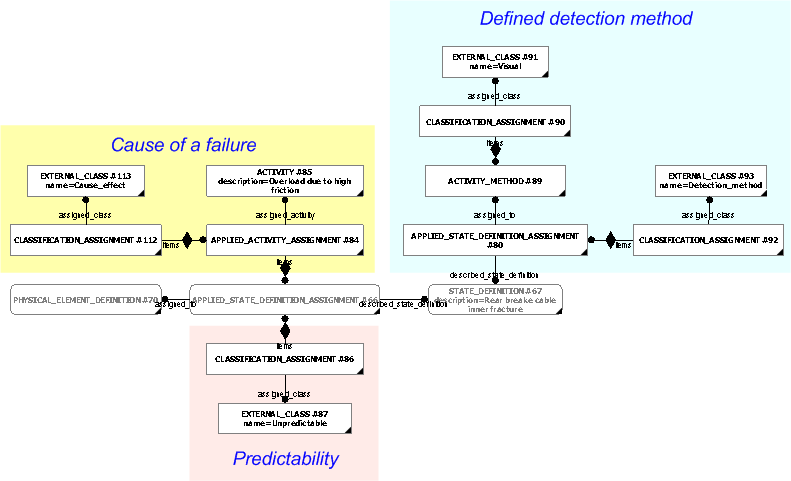
Context
The identification of the context for which the failure mode is valid, may be defined as one or more of the following:
Classification
Each consequence is represented as a
State_definition.
The relationship between the
State_definition
representing the failure mode (relating) and the
State_definition
representing the consequence (related) is established using a
State_definition_relationship.
The State_definition
representing the consequence should be classified as [Consequence]![]() Error RDL1: The class Consequence does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Consequence does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The State_definition_relationship
should be classified to reflect the type of cause effect relationship.
Typical values include [Local_effect]![]() Error RDL1: The class Local_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Local_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
,
[Next_higher_effect]![]() Error RDL1: The class Next_higher_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Next_higher_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and [End_effect]![]() Error RDL1: The class End_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class End_effect does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Each State_definition_relationship
may also be classified to reflect whether the consequence is [Primary]![]() Error RDL1: The class Primary does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Primary does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
or [Secondary]![]() Error RDL1: The class Secondary does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Secondary does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
Each State_definition
representing the consequence may also be classified to reflect whether it is
[Hidden]![]() Error RDL1: The class Hidden does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Hidden does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
or [Evident]![]() Error RDL1: The class Evident does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Evident does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
NOTE More advanced relationships including conditions can be defined using the C026: representing_condition capability.
Description
The State_definition. description attribute should contain a textual description of the consequence.
Reference to affected functions, systems etc
Each State_definition
representing a consequence may being assigned
to a
Functional_element or a
System_element
using
Applied_state_definition_assignment.
The Functional_element /
System_element being
assigned with a consequence, may be referenced as described in the
referencing_product_breakdown_element![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_product_breakdown_element not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_product_breakdown_element not in dex_index.xml
capability.
NOTE
The respective breakdown element/part in the breakdown is referenced by its identifier.
Each identification should be classified. Typical values are
[LCN_code]![]() Error RDL1: The class LCN_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class LCN_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
, [Name_identification]![]() Error RDL1: The class Name_identification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Name_identification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The Applied_state_definition_assignment
should be classified as
[Affected_item]![]() Error RDL1: The class Affected_item does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Affected_item does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
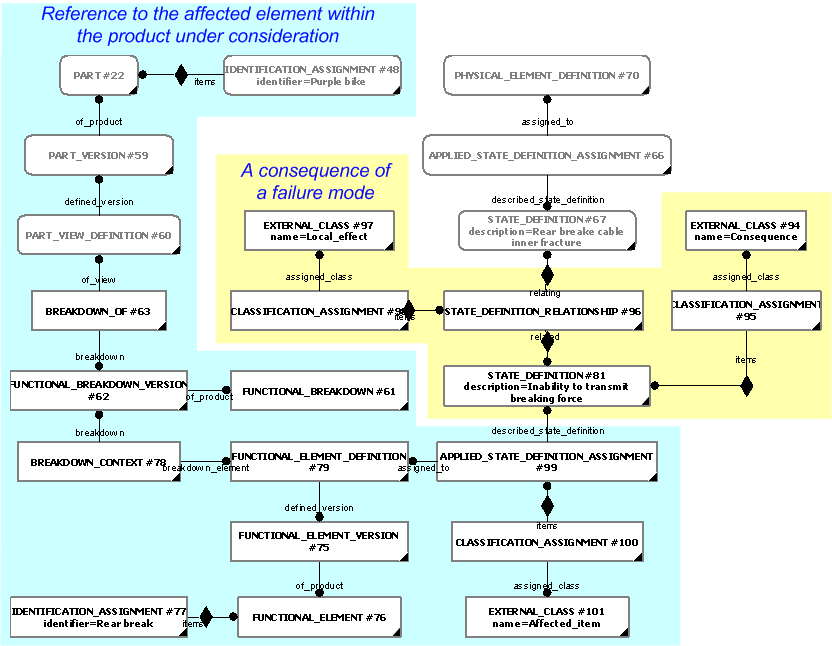
Severity
Severity is represented as additional classifications of the State_definition representing the consequence. Typical values include:
Likelihood
The representation of likelihood may be defined as one of the following:
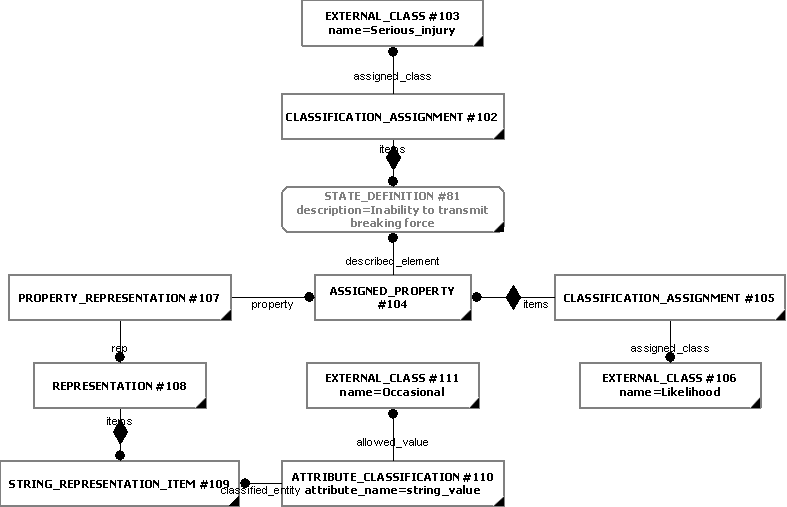
Criticality code
Even though the criticality code may be derived from the combination of severity
and likelihood, it may still be explicitly exchanged as an
Assigned_property.
The
Assigned_property
should be assigned to the
State_definition
representing the consequence. The
Assigned_property
should be classified as [Criticality_code]![]() Error RDL1: The class Criticality_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Criticality_code does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The String_representation_item.
string_value
attribute representing the qualifier value should be classified using
Attribute_classification,
as described in the C010: assigning_reference_data capability.
A note is represented as a Assigned_property as described in the C076: assigning_product_properties and C080: representing_properties_textually capabilities. The Assigned_property can be assigned to the either the State_definition representing the failure mode or the State_definition representing the consequence. The Assigned_property should be classified as "Note" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Note).
The definition of a fully acceptable, degraded and fault state are all represented as Conditions being assigned to the State_definition representing the failure mode.
The Condition_assignment should be
classified to reflect the type of condition. Typical values include
[Acceptable_state_definition]![]() Error RDL1: The class Acceptable_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Acceptable_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
,
[Degraded_state_definition]![]() Error RDL1: The class Degraded_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Degraded_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
and
[Fault_state_definition]![]() Error RDL1: The class Fault_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Fault_state_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
NOTE A typical condition could be the value of a temperature property. The temperature property would the be identified as a condition parameter. This requires the usage of the C076: assigning_product_properties, C079: representing_properties_numerically and C084: representing_property_value_ranges capabilities.
© OASIS 2010 — All rights reserved