Template:— representing_person_typical (rep_pers_typ)
Capability:representing_person_organization_typical
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) The use of this template is deprecated.
(2008-01-25 Until further notice) The use of this template is deprecated.
(2008-01-25 Until further notice)
|
Date: 2008/02/21 16:29:46
Revision: 1.7
|
Deprecation: Template representing_person_typical
The use of template,representing_person_typical, has been deprecated since 2008-01-25 Until further notice.
This section specifies the template representing_person_typical.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of the capability
representing_person_organization_typical
which provides an overall description of the
relevant parts of the ISO 10303-239 information model and a description
of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
Note:
This template is subject for change, and therefore being deprecated until further notice. The current content of this template
has been copied to the template
referencing_person_typical.
This template describes how to represent a type of person without its definition.
NOTE
The Type_of_person_definition
has been omitted from this template. The definition(s) for a type of person should be defined within the class (reference
data)
being used to determine the type of person.
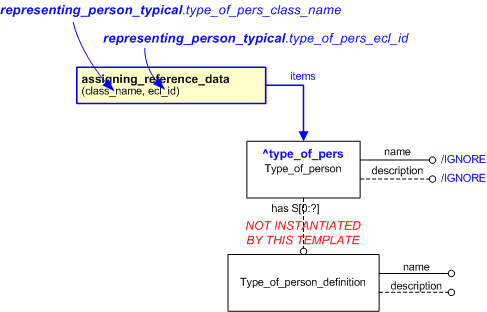
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_person_typical".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_person_typical
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_person_typical template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the type of person being referenced.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Type_of_person
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Type_of_person
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $representing_person_typical.type_of_pers%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Type of person
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
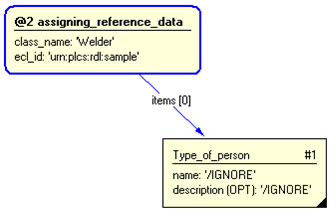
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_person_typical template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_person_typical template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = TYPE_OF_PERSON('/IGNORE','/IGNORE',());
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Welder','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
28 ed.2 syntax) is:
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_person_typical template
The following section details how the
representing_person_typical
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning descriptor
NOTE this characterization is optional.