| Capability (C051):— representing_person_organization_typical |
Date: 2008/02/01 09:26:08
Revision: 1.22
|
Types of persons or organizations are categories of people or organizations having common characteristics or notional persons
or organizations considered as a representative of such categories. In the context of this part of ISO10303, types of persons
are defined chiefly in terms of experience and qualifications. Again, types of experience and qualifications are categories
of experience and qualifications having common characteristics.
EXAMPLE
An academic institution is an example of a type of organization.
EXAMPLE
A university degree is an example of a type of qualification.
EXAMPLE
A pilot is an example of a type of person.
EXAMPLE
Flying experience is an example of a type of experience.
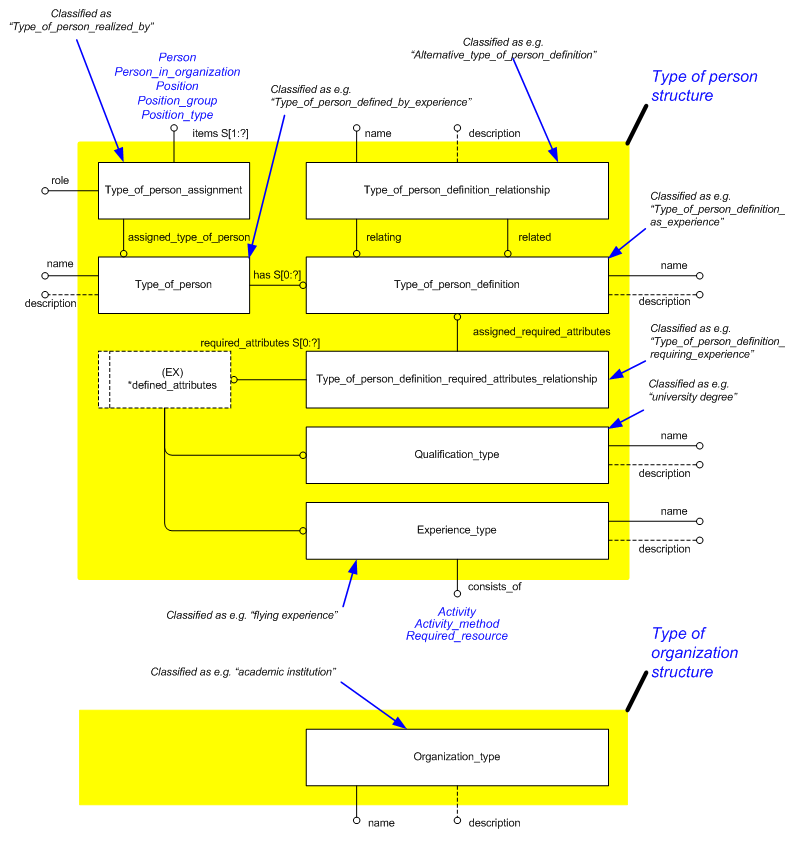
The EXPRESS-G for the approval model is shown in Figure 1 below and explained in the following sections.
NOTE 1
The EXPRESS-G is not complete. For the complete EXPRESS see the modules:
Organization type and
Type of person.
Figure 1 — Representing representing person organization typical EXPRESS-G
The starting point for Type_of_person is Type_of_person_definition, which is the collector of the criteria used to define
a Type_of_person. These criteria can be defined in terms of properties of the person, such as maximum height, or in terms
of Experience or Qualification, and for an actual Person to qualify as meeting the Type_of_person_definition, they must meet
all these criteria.
A Type_of_person is then a person meeting one or more of Type_of_person_definition. (The properties of Type_of_person_definition
are ANDed, while the Type_of_person to Type_of_person_definition links are ORed, effectively allowing any combination of
properties and experience). A Type_of_person without any definition is defined by the name and description.
It is also possible to relate one Type_of_person_definition to another, with the role of the relationship being defined
by classification. The relationship Type_of_person_assignment is not currently used.
The concept of a qualification, such as "exam passed" is recorded though Qualification_type. A Qualification
Many of the constructs shown in Figure 1 can be characterized; which is to say that they may have approvals, classifications, conditions, dates or times, identifiers, justifications,
persons or organizations, or properties assigned to them. The following sections detail the characterization of resource objects.
Approvals of
types of qualifications, experience, and persons
or of
person type assignments
are represented by the assignment of
Approval
objects to
Experience_type,
Qualification_type,
Type_of_person, and
Type_of_person_assignment
objects using
Approval_assignment
objects.
NOTE 1
The assignment of approvals is described in the capability:
C019: assigning_approvals.
The classification of
types of qualifications, experience, and persons
or of
person type assignments
is represented by the assignment of
External_class
objects to
Experience_type,
Qualification_type,
Type_of_person,
Type_of_person_assignment,
Type_of_person_definition,
Type_of_person_definition_required_attributes_relationship, and
Type_of_person_definition_relationship
objects using
Approval_assignment
objects.
The date and/or time on/at which a relationship is established between a type of person and a particular person or a position
within an organization is represented by the assignment of
Date_time
objects or
Calendar_date
objects to
Type_of_person_assignment
objects using
Date_or_date_time_assignment
objects.
NOTE 2
The assignment of date and times is described in the capability:
C036: assigning_date_time.
The identification of types of experience, organization, qualification, and person is achieved by the linking of
Identification_assignment
objects to
Experience_type,
Organization_type,
Qualification_type, and
Type_of_person
objects.
NOTE 3
The assignment of approvals is described in the capability:
C001: assigning_identifiers.
Locations of types of organizations and persons are represented by the assignment of
Location
objects to
Organization_type and
Type_of_person
objects using
Location_assignment
objects.
The responsibility for specifying a type of qualification or for establishing a relationship between a type of person
and a particular person or a position within an organization is represented by the assignment of
Organization and
Person_in_organization
objects to
Qualification_type and
Type_of_person_assignment
objects using
Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment
objects.
The following sections define a set of templates for the capability,
where a template is a specification of a set of entities that need to
be instantiated to represent a given set of information.
This section specifies the template referencing_person_typical.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
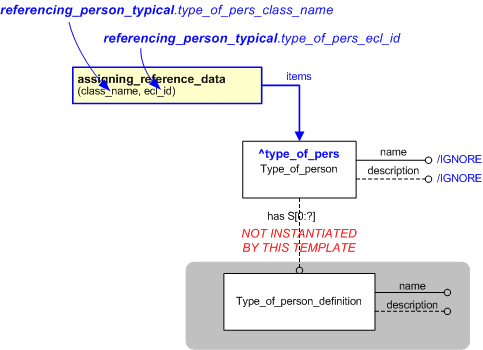
This template describes how to reference a type of person by its class name.
NOTE
The Type_of_person_definition
has been omitted from this template.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"referencing_person_typical".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for referencing_person_typical
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the referencing_person_typical template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the type of person being referenced.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Type_of_person
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Type_of_person
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $referencing_person_typical.type_of_pers%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Type of person
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
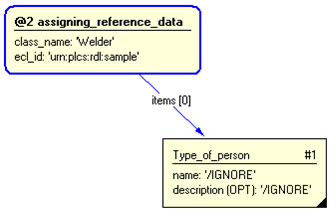
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/referencing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated referencing_person_typical template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by referencing_person_typical template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = TYPE_OF_PERSON('/IGNORE','/IGNORE',());
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Welder','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
28 ed.2 syntax) is:
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/referencing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of referencing_person_typical template
The following section details how the
referencing_person_typical
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning descriptor
NOTE this characterization is optional.
This section specifies the template representing_person_typical.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
Deprecation: Template representing_person_typical
The use of template,representing_person_typical, has been deprecated since 2008-01-25 Until further notice.
Note:
This template is subject for change, and therefore being deprecated until further notice. The current content of this template
has been copied to the template
referencing_person_typical.
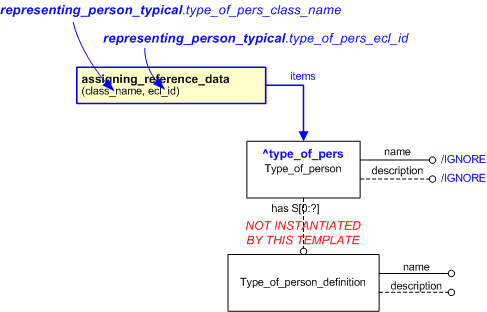
This template describes how to represent a type of person without its definition.
NOTE
The Type_of_person_definition
has been omitted from this template. The definition(s) for a type of person should be defined within the class (reference
data)
being used to determine the type of person.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_person_typical".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_person_typical
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_person_typical template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the type of person being referenced.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Type_of_person
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Type_of_person
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $representing_person_typical.type_of_pers%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Type of person
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_person_typical template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_person_typical template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = TYPE_OF_PERSON('/IGNORE','/IGNORE',());
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Welder','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
28 ed.2 syntax) is:
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_person_typical(type_of_pers_class_name='Welder', type_of_pers_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_person_typical template
The following section details how the
representing_person_typical
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning descriptor
NOTE this characterization is optional.
This section specifies the template representing_organization_typical.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a type of organization, e.g. line of maintenance.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_organization_typical".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
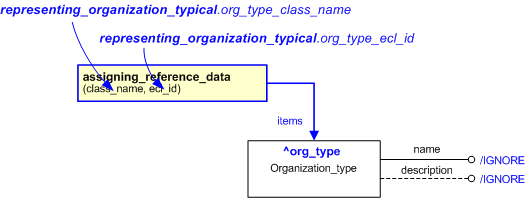
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_organization_typical
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_organization_typical template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the organization type being referenced.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Organization_type
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_organization_typical.org_type%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Organization type
Each instance of the
entity
(
Organization_type)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_organization_typical) namely:
org_type_class_name,
org_type_ecl_id.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
org_type.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
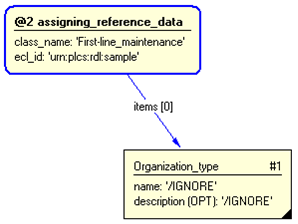
/representing_organization_typical(org_type_class_name='First-line_maintenance', org_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_organization_typical template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_organization_typical template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = ORGANIZATION_TYPE('/IGNORE','/IGNORE');
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#5,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','First-line_maintenance','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_organization_typical(org_type_class_name='First-line_maintenance', org_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_organization_typical template
The following section details how the
representing_organization_typical
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning descriptor
NOTE this characterization is optional.
This section specifies the template representing_experience_type.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a type of experience.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_experience_type".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
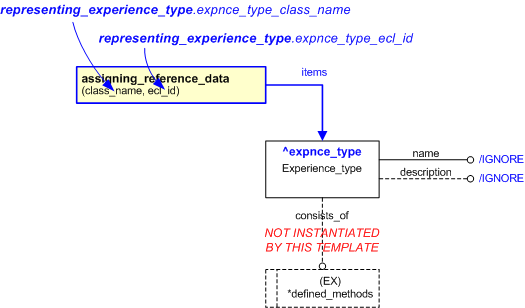
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_experience_type
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_experience_type template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the type of qualification being represented.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Experience_type
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_experience_type.expnce_type%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Experience_type
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
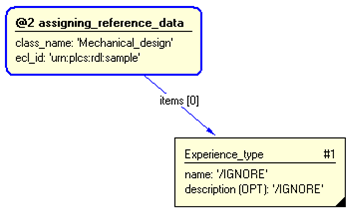
/representing_experience_type(expnce_type_class_name='Mechanical_design', expnce_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_experience_type template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_experience_type template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = EXPERIENCE_TYPE('/IGNORE','/IGNORE',$);
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#5,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Mechanical_design','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
28 ed.2 syntax) is:
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_experience_type(expnce_type_class_name='Mechanical_design', expnce_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_experience_type template
The following section details how the
representing_experience_type
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning code
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A Experience_type may also be determined by
codes as described in the template assigning_code. A description of
the code used to determine the experience type may then be provided as a description associated with the code, as
described
under the assigning_code template characterization section.
NOTE
The assignment of codes is described the capability C093: assigning_codes.
This section specifies the template representing_qualification_type.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a type of qualification.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_qualification_type".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
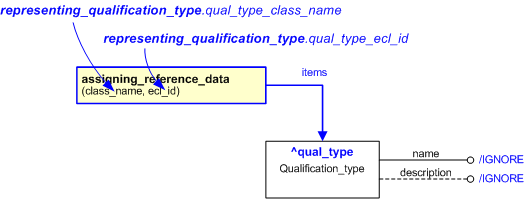
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_qualification_type
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_qualification_type template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the
External_class that determines the type of qualification being represented.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Qualification_type
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_qualification_type.qual_type%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Qualification_type
Each instance of the
entity
(
Qualification_type)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_qualification_type) namely:
qual_type_class_name,
qual_type_ecl_id.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
qual_type.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
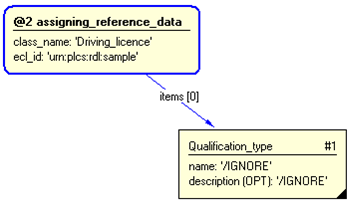
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_qualification_type(qual_type_class_name='Driving_licence', qual_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_qualification_type template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_qualification_type template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = QUALIFICATION_TYPE('/IGNORE','/IGNORE');
#3 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#5,(#1),'/IGNORE');
#5 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Driving_licence','/IGNORE',#6);
#6 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample',$);
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
28 ed.2 syntax) is:
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_qualification_type(qual_type_class_name='Driving_licence', qual_type_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_qualification_type template
The following section details how the
representing_qualification_type
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning code
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A Qualification_type may also be determined by
codes as described in the template assigning_code. A description of
the code used to determine the qualification type may then be provided as a description associated with the code,
as described
under the assigning_code template characterization section.
NOTE
The assignment of codes is described the capability C093: assigning_codes.
This capability
"Representing a type of person and organization" is related to the
following capabilities:
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error C1: Capability referencing_person_organization not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_person_organization not in dex_index.xml
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error C1: Capability referencing_person_organization_typical not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_person_organization_typical not in dex_index.xml
- C016: representing_person_organization
This capability
"Representing a type of person and organization" is dependent on
the following capabilities:
The following classes of reference data are required for this capability:
[Type_of_person_realized_by]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_realized_by does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_realized_by does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_defined_by_experience]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_defined_by_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_defined_by_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_defined_by_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_defined_by_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_defined_by_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_definition_as_experience]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_as_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_as_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_definition_as_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_as_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the
dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_as_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the
dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Alternative_type_of_person_definition]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Alternative_type_of_person_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Alternative_type_of_person_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Superseding_type_of_person_definition]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Superseding_type_of_person_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Superseding_type_of_person_definition does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_definition_requiring_experience]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_requiring_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check
the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_requiring_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check
the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Type_of_person_definition_requiring_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_requiring_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check
the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Type_of_person_definition_requiring_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check
the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Commercial_organization]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Commercial_organization does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Commercial_organization does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Non_commercial_organization]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Non_commercial_organization does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Non_commercial_organization does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Academic_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Academic_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Academic_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Vocational_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Vocational_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Vocational_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Professional_qualification]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Professional_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Professional_qualification does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Professional_or_vocational_experience]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Professional_or_vocational_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Professional_or_vocational_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
[Skill_based_experience]
![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Skill_based_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Skill_based_experience does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml