Template:— risk_realization (rsk_rlzn)
Context:— UK_Defence |
Date: 2010/03/15 15:08:44
Revision: 1.3
|
This section specifies the template risk_realization.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of
UK_Defence.
Refer to the business context for details of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent the concept of risk realization in terms of PLCS model elements (templates, entities
and reference data).
A risk realization is a record of a risk actually occurring.
This information object represent the record of the realization of a anticipated risk through the occurrance of an event.
Figure 1 — A MOOD Business Architect representation of the Business Object: Risk realization
The attributes of the Risk realization object are tabled below.
|
Attribute name
|
Attribute description
|
Attribute type
|
Optionality
|
| Anticipated risk |
This is the reference to the risk that has been realized by the causal event occurring. |
Risk |
Mandatory |
| Causal event |
This is the reference to the event that caused the anticipated risk to be realized. |
Event |
Mandatory |
| ID |
This is the identifier of the Risk realization. |
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
Table 1 — Risk realization attribute details
NOTE
This template is dependent on entities in the ISO10303-239 Edition 2 schema.
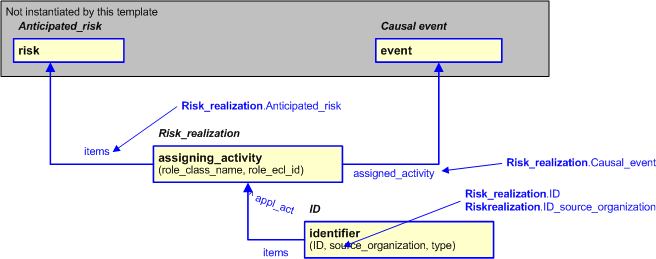
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"risk_realization".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 2 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for risk_realization
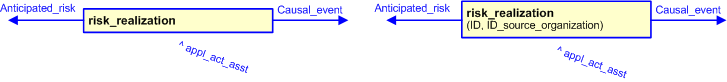
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
Figure 3 — The graphical representation of the risk_realization template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
Anticipated_risk (Type=
'ENTITY
(
![[warning:]]() Error ER1: The entity Risk does not exist
Error ER1: The entity Risk does not existRisk)'
![[warning:]]() Error EXP-1: The EXPRESS entity Risk
Error EXP-1: The EXPRESS entity Risk
does not exist in data/schemas/ap239_arm_lf.xml.)
This is the reference to the risk that has been realized by the causal event occurring.
This is the reference to the event that caused the anticipated risk to be realized.
This is the identifier of the Risk realization.
The organization that created the associated identifier. Additionally
a Person or Information System could be defined when either of these are the source; see Identifier template characterizations
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
%^target = $risk_realization.appl_act_asst%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Risk realization
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
-- Assigning_activity /
assigning_activity(
items=@Anticipated_risk,
assigned_activity=@Causal_event,
role_class_name='Risk_realization',
role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
%^appl_act_asst = $assigning_activity.appl_act%
-- Identify the risk_realization /
identifier(
ID=@ID,
source_organization=@ID_source_organization,
type='ID',
items=^appl_act_asst)/
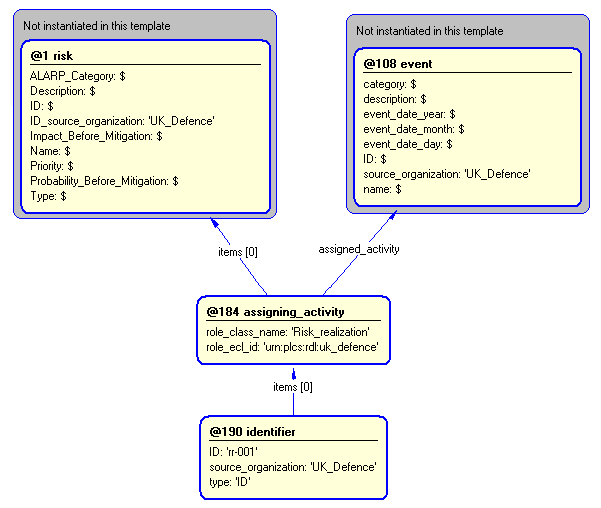
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
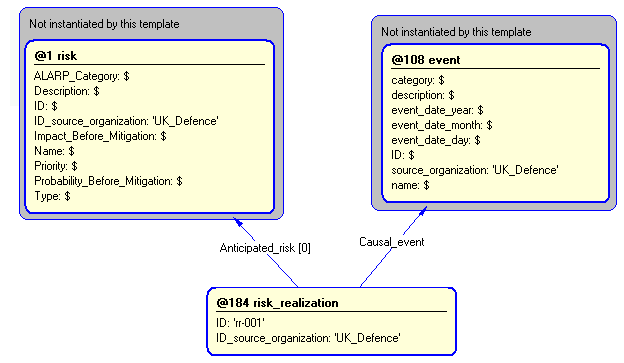
/risk_realization(Anticipated_risk='#r', Causal_event='#e', ID='rr_001', ID_source_organization='UK_Defence')/
(an illustration of the consolidated risk_realization template is shown in
Figure
5 below.)
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by risk_realization template
The instance diagram in
Figure
5
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/risk_realization(Anticipated_risk='#r', Causal_event='#e', ID='rr_001', ID_source_organization='UK_Defence')/
Figure 5 — Instantiation of risk_realization template
Characterizations
No common characterizations of the template
risk_realization
have been identified. However, the ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model
may enable other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.