Template:— product_composition (prod_comp)
Context:— UK_Defence |
Date: 2009/04/17 10:48:48
Revision: 1.2
|
This section specifies the template product_composition.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of
UK_Defence.
Refer to the business context for details of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a UK_Defence product composition, using
Assembly_component_relationship.
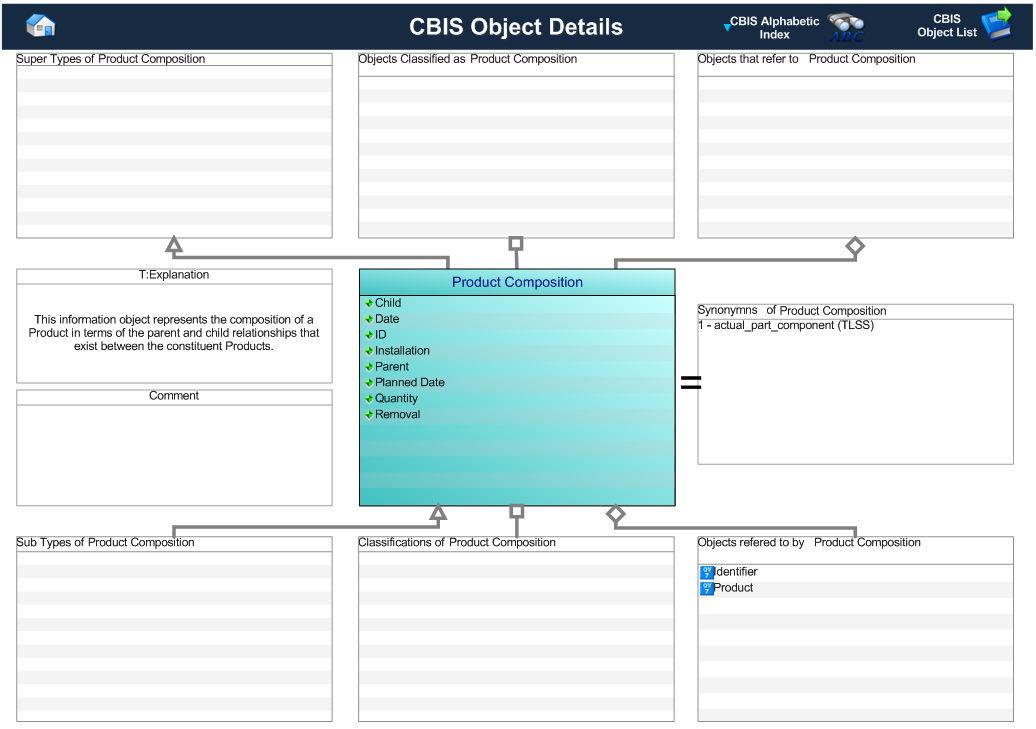
This information object represents the composition of a Product in terms of the parent and child
relationships that exist between the constituent Products.
For further information about the representation of a product composition, see below.
This information object represents the composition of a Product in terms of the parent and child
relationships that exist between the constituent Products.
Individual products are typically identified by a serial number.
Figure 1 — Graphical Representation for Business Object Product Composition
Record:
This information object represents the information about a Product Composition.
|
Attribute name
|
Attribute description
|
Attribute type
|
Optionality
|
| Child |
This is the reference to the child in the relationship ie. that Product which is installed, or which it is removed. |
Product |
Mandatory |
| Date |
This is the date and time on which the child was installed in or removed from the
parent.
|
Intrinsic |
Optional |
| ID |
This is the identifier of the product composition. |
Identifier |
Mandatory |
| Installation |
This is an indicator of whether the product composition relationship represents an installation of the child within the parent. |
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| Parent |
This is the reference to the parent in the relationship ie. that Product in which the related child Product is installed,
or from which it is removed.
|
Product |
Mandatory |
| Planned Date |
This is the date and time on which the child is planned to be installed in or removed from the
parent.
|
Intrinsic |
Optional |
| Quantity |
This is the quantity of the child that was installed on or removed from the parent. |
Identifier |
Optional |
| Removal |
This is an indicator of whether the actual product composition relationship represents a removal of the child from the parent. |
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
Table 1 — Product attribute details
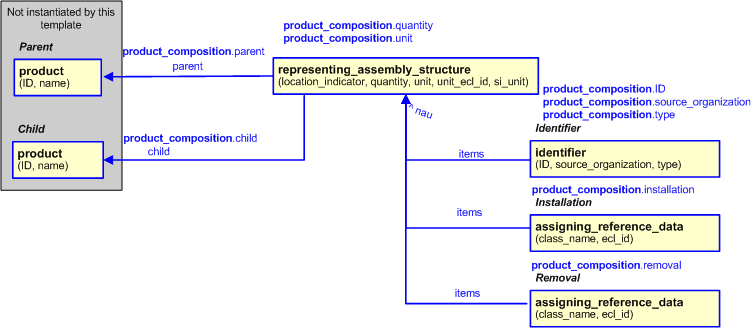
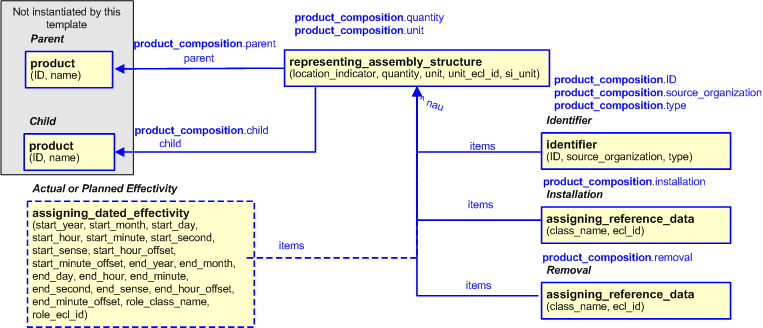
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"product_composition".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 2 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for product_composition
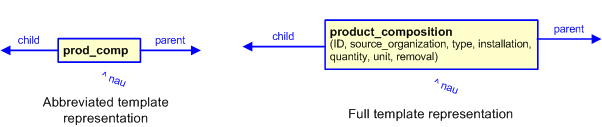
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
Figure 3 — The graphical representation of the product_composition template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
This is the reference to the child in the relationship ie. that Product which is installed, or which it is removed.
This is the identifier of the product composition
The organization that created the associated identifier. Additionally
a Person or Information System could be defined when either of
these are the source; see Identifier template characterizations
This is the name of the type of the class used to classify the identifier and so
provide the role or reason for the identification.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
This is an indicator of whether the product composition relationship represents an installation of the child within
the parent
This is the reference to the parent in the relationship ie. that Product in which the related child Product is installed,
or from which it is removed.
The quantity of the child in parent assembly. If unspecified, '1' is assumed.
The class name of the unit in which the value is expressed.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
This is an indicator of whether the product composition relationship represents a removal of the child within the
parent
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Next_assembly_usage
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $product_composition.nau%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Unique assembly
Each instance of the
entity
(
Next_assembly_usage)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (product_composition) namely:
parent,
child,
ID.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
nau.
The parent and child(ren) should only occur once in a data set.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
/
representing_assembly_structure(
parent=@parent,
child=@child,
location_indicator='/IGNORE',
quantity=@quantity,
unit=@unit,
unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
si_unit='false')/
%^composition = $representing_assembly_structure.nau%
-- instantiate assigning_identification for the product compositions identifier /
identifier(
ID=@ID,
source_organization=@source_organization,
type=@type,
items=^composition)/
-- Assign installation indicator /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^composition,
class_name=@installation,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- Assign removal indicator /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^composition,
class_name=@removal,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
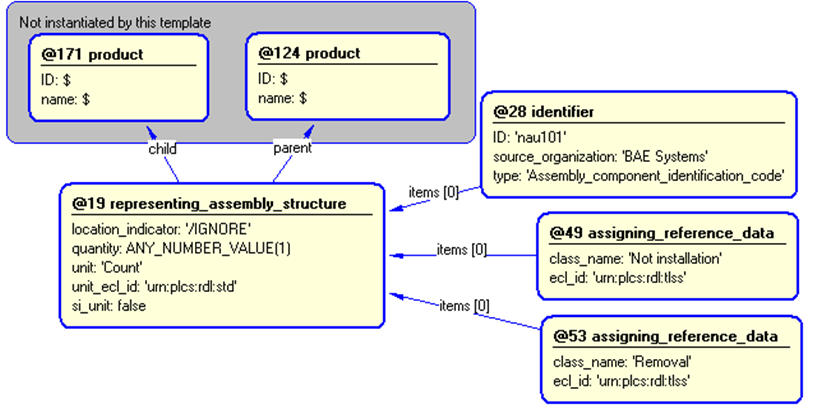
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
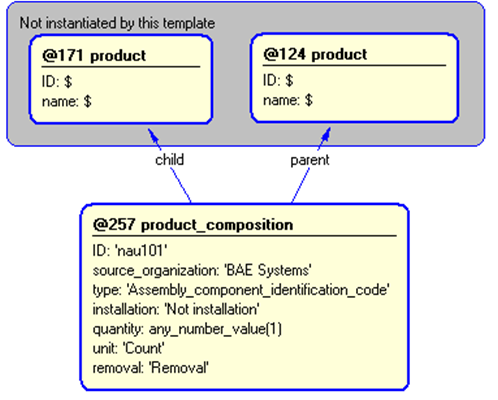
/product_composition(child='@171', id='nau101', source_organization='BAE Systems', type='Identification_code', installation='Not installation', parent='@124', removal='Removal')/
(an illustration of the consolidated product_composition template is shown in
Figure
5 below.)
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by product_composition template
The instance diagram in
Figure
5
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/product_composition(child='@171', id='nau101', source_organization='BAE Systems', type='Identification_code', installation='Not installation', parent='@124', removal='Removal')/
Figure 5 — Instantiation of product_composition template
The following section details how the
product_composition
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in Figure
6
shows the possible characterizations of the template
"product_composition".
Figure 6 — Characterizations for product_composition
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning effectivity
NOTE this characterization is optional.
An effectivity may be assigned to the Next_assembly_usage.
This shall be done using entity Effectivity_assignment.
For example, a dated effectivity shall be assigned using template assigning_dated_effectivity
this could represent the planned or actual effectivity by classifying the role as
"Actual effectivity"
(urn:plcs:rdl:std:Actual effectivity)
or
"Effectivity target"
(urn:plcs:rdl:std:Effectivity target).
NOTE
The assignment of effectivities is described in capability C006: assigning_effectivity.
/assigning_dated_effectivity(start_year='2008', start_month='03', start_day='13', start_hour='0', start_minute='0', start_second='0', start_sense='.EXACT.', start_hour_offset='0', start_minute_offset='0', end_year='2008', end_month='12', end_day='31', end_hour='0', end_minute='0', end_second='0', end_sense='.EXACT.', end_hour_offset='0', end_minute_offset='0', role_class_name='Planned_effectivity', role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', items='#218')/