Template:— hazard (hzd)
Context:— UK_Defence |
Date: 2010/03/15 14:46:02
Revision: 1.3
|
This section specifies the template hazard.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of
UK_Defence.
Refer to the business context for details of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
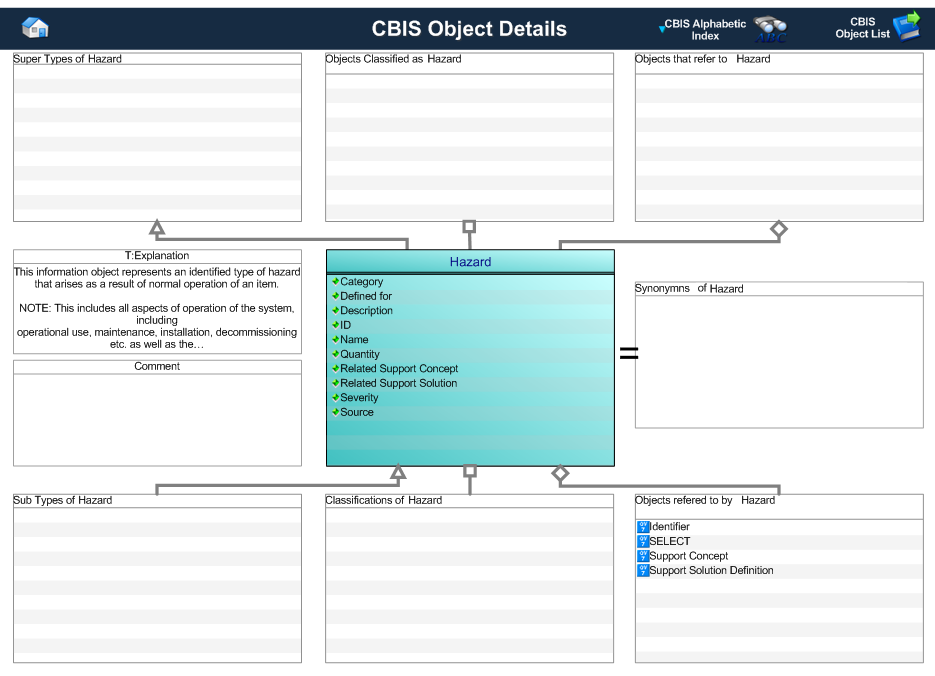
This template describes how to represent the CBIS definition of a Hazard.
Figure 1 — Graphical Representation for Business Object Hazard
Hazard
This information object represents information about an identified hazard arising as a result of normal operation of an item.
NOTE
This includes all aspects of operation of the system, including
operational use, maintenance, installation, decommissioning etc. as well as the
potential impact on indirect uses and users, such as the effect on bystanders. It also includes different states of system
operation and the conditions which
emerge as a result of those different states.
|
Attribute name
|
Attribute description
|
Attribute type
|
Optionality
|
| Category |
This is the category of the health hazard.
|
Intrinsic |
Optional |
| Defined_for |
This is the reference to the usage context of the item, or a task, for which the hazard is defined. |
SELECT of Task, Product Role, or Required PSE Constituent Usage Pattern |
Mandatory |
| Description |
This is the description of the hazard. |
intrinsic |
Optional |
| ID |
This is the identifier of the hazard. |
Relationship to Identifier |
Mandatory |
| Name |
This is the name of the hazard. |
intrinsic |
Optional |
| Quantity |
This is the quantification of the hazard category that has been identified as being caused by the source. |
Intrinsic |
Optional |
| Related Support Concept |
This is a reference to the related support concept. |
Relationship to Support Concept |
Mandatory |
| Related Support Solution |
This is a reference to the related support solution. |
Relationship to Support Solution Definition |
Mandatory |
| Severity |
This is the severity category of the hazard. |
Intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| Source |
This is the reference to the source of the hazard. |
SELECT of Property or Environmental Characteristic |
Mandatory |
Table 1 — Hazard attribute details
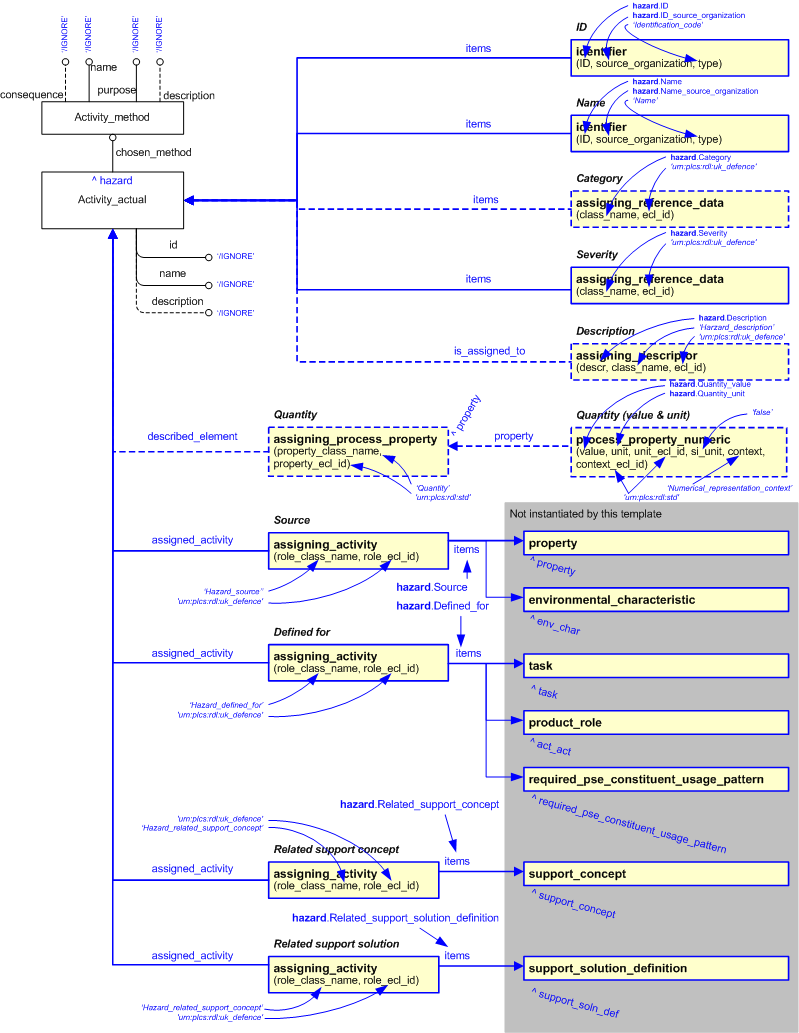
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"hazard".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
The diagram below shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required to represent the template "Hazard". The text
highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 2 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for hazard
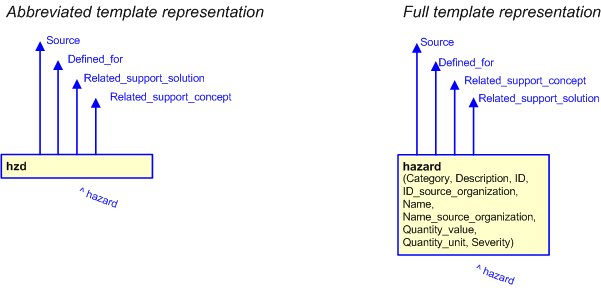
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
Figure 3 — The graphical representation of the hazard template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The category of the health hazard.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Hazard_category]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
The reference to the usage context of the item, or a task, for which the hazard is defined.
The description of the health hazard.
This is the identifier of the health hazard.
The organization that created the identifier. Additionally
a Person or Information System could be defined when either of these are the source; see Identifier template.
This is the name of the health hazard.
The organization that created the name.
This is the quantification of the related health hazard category that has been identified as being caused by the source.
The class name of the unit in which the quantity is expressed.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The reference to the support concept for which the hazard is defined.
The reference to the support solution for which the hazard is defined.
This is the severity category of the hazard.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Severity_category]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
This is the reference to the source of the health hazard.
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Activity_actual
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $hazard.hazard%
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
-- Activity_method (instantiated but not used) Activity_methodActivity_method.name = '/IGNORE'
Activity_method.description = '/IGNORE'
Activity_method.consequence = '/IGNORE'
Activity_method.purpose = '/IGNORE'
%^hazard_method =
Activity_method%
-- Activity_actual Activity_actualActivity_actual.id = '/IGNORE',
Activity_actual.name = '/IGNORE'
Activity_actual.description = '/IGNORE'
Activity_actual.chosen_method ->
^hazard_method
%^hazard =
Activity_method%
%^hazard =
Activity_actual%
-- [optional Category] /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^hazard,
class_name=@Category,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- Defined_for (assigning_activity) /
assigning_activity(
role_class_name='Hazard_defined_for',
role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
assigned_activity=^hazard,
items=@Defined_for)/
-- ID /
identifier(
ID=@ID,
source_organization=@ID_source_organization,
type='Identification_code',
items=^hazard)/
-- Name /
identifier(
ID=@Name,
source_organization=@Name_source_organization,
type='Name',
items=^hazard)/
-- assign quantity /
assigning_process_property(
property_class_name='Quantity',
property_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
described_element=^hazard)/
%^property = $assigning_process_property.property%
-- [Optional Quantity] /
process_property_numeric(
value=@Quantity_value,
unit=@Quantity_unit,
unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
si_unit='false',
context='Numerical_representation_context',
context_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
property=^property)/
-- Category /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^hazard,
class_name=@Category,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- Related support concept /
assigning_activity(
role_class_name='Hazard_related_support_concept',
role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
assigned_activity=^hazard,
items=@Related_support_concept)/
-- Related support solution /
assigning_activity(
role_class_name='Hazard_related_support_solution',
role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
assigned_activity=^hazard,
items=@Related_support_solution)/
-- Severity /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^hazard,
class_name=@Severity,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- Source (assigning_activity) /
assigning_activity(
role_class_name='Hazard_source',
role_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
assigned_activity=^hazard,
items=@Source)/
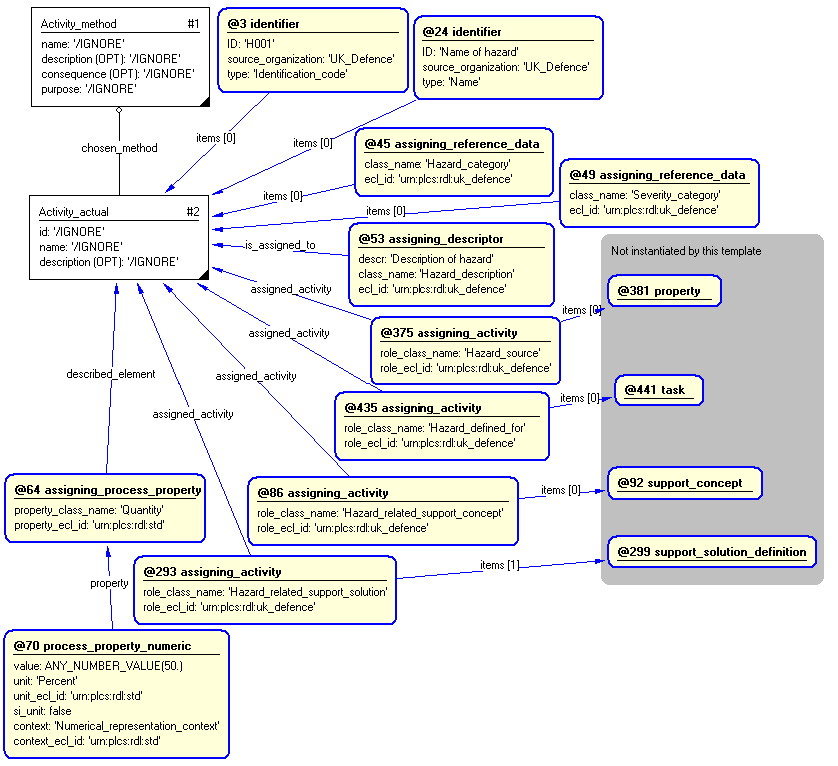
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
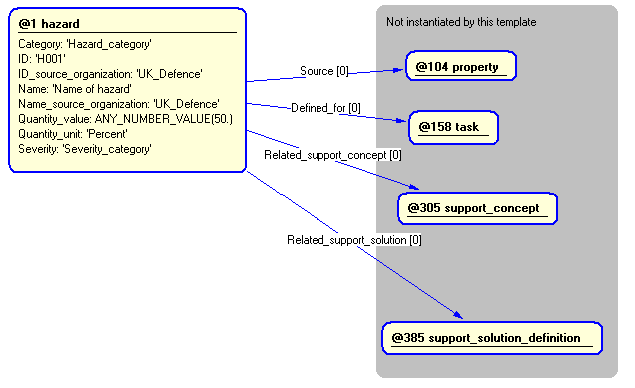
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/hazard(Category='Hazard_category', Defined_for='@158', Description='Description of hazard', ID='H001', ID_source_organization='UK_Defence', Name='Name of hazard', Name_source_organization='UK_Defence', Quantity_value='50', Quantity_unit='Percent', Related_support_concept='@305', Related_support_solution='@385', Severity='Severity_category', Source='@104')/
(an illustration of the consolidated hazard template is shown in
Figure
5 below.)
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by hazard template
The instance diagram in
Figure
5
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/hazard(Category='Hazard_category', Defined_for='@158', Description='Description of hazard', ID='H001', ID_source_organization='UK_Defence', Name='Name of hazard', Name_source_organization='UK_Defence', Quantity_value='50', Quantity_unit='Percent', Related_support_concept='@305', Related_support_solution='@385', Severity='Severity_category', Source='@104')/
Figure 5 — Instantiation of hazard template
Characterizations
No common characterizations of the template
hazard
have been identified. However, the ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model
may enable other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.