Template:— representing_geographical_location (rep_geo_locn)
Capability:representing_location |
Date: 2005/08/15 08:20:35 :
Revision: 1.15
|
This section specifies the template representing_geographical_location.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of the capability
representing_location
which provides an overall description of the
relevant parts of the ISO 10303-239 information model and a description
of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
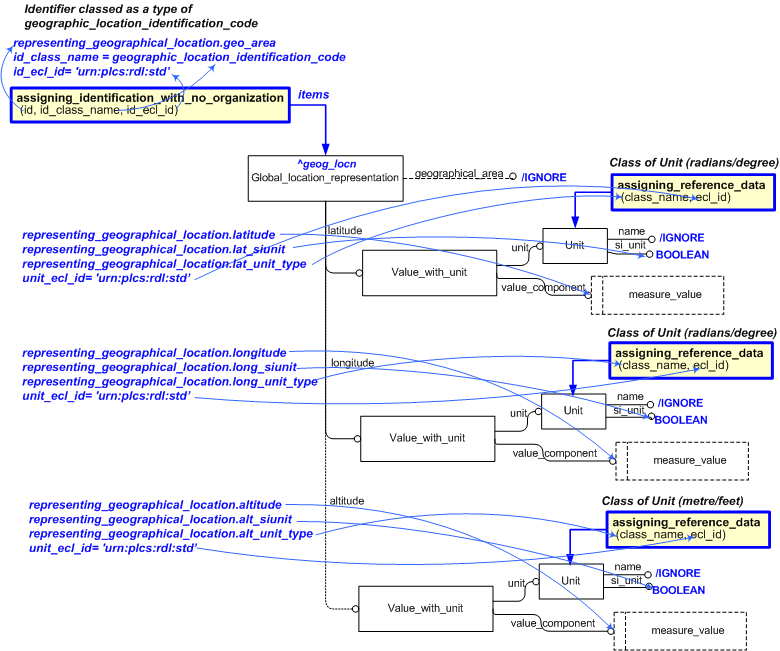
This template describes the representation of a global location representation.
It instantiates an instance of global_location_representation and upto 3 numerical items within this template.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_geographical_location".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — Base Template Configuration for Representing Global Location Representation
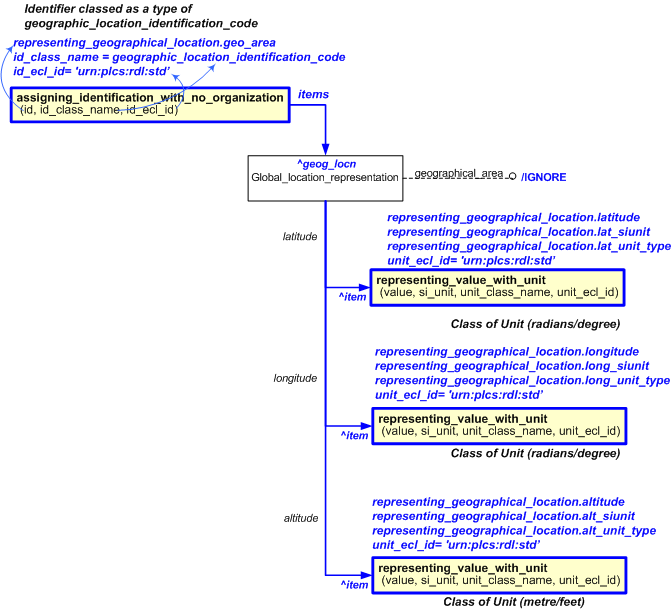
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_geographical_location".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 2 — Abstracted Template Configuration for Representing Global Location Representation
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
Figure 3 — Template for Representing Global Location Representation
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The latitude measurement.
The class name of the corresponding to the latitude units (radian or degree).
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Radian]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Radian does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Degree]
Error RDL1: The class Radian does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Degree]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Degree does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Degree does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Are the coordinates for latitude measured in SI Units (True/False)?
The longitude measurement
The class name of the corresponding to the longitudinal units (radian or degree).
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Radian]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Radian does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Degree]
Error RDL1: The class Radian does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Degree]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Degree does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Degree does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Are the coordinates for longitude measured in SI Units (True/False)?
The altitude measurement - optional
The class name of the corresponding to the altitude units (metre or feet).
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Metre]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Metre does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Feet]
Error RDL1: The class Metre does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Feet]![[warning:]](../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL1: The class Feet does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Feet does not exist in RDL at urn urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Are the coordinates for altitude measured in SI Units (True/False)?
geo_area (Default='Unknown',Type='STRING', Optional)
The geographic area name is assigned via ref data - optional
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
%^target = $representing_geographical_location.geog_locn%
For example, to create additional identifiers or classification for an instance of
Global_location_representation
. E.g.
-- The template representing_geographical_location has an external reference
-- geog_locn. It can now be the target for assignments e.g.
%^todays_location = $representing_geographical_location.geog_locn%
-- e.g assign 'wilderness' to the global_location_representation in the role of "Geographic_area"
/assigning_identification_with_no_organization(items=^geog_locn,
id='Wilderness',
id_class_name='Geographic_area',
id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
-- Create Global location rep %^geog_locn =
Global_location_representation%
Global_location_representation.geographical_area = '/IGNORE'
-- set the latitude value /
representing_value_with_unit(
unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
si_unit=@lat_siunit,
value=@latitude,
unit=@lat_unit_type)/
%^loc_lat = $representing_value_with_unit.value%
Global_location_representation.latitude ->
^loc_lat
-- set the longitude value /
representing_value_with_unit(
unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
si_unit=@long_siunit,
value=@longitude,
unit=@long_unit_type)/
%^loc_long = $representing_value_with_unit.value%
Global_location_representation.longitude ->
^loc_long
-- set the altitude value /
representing_value_with_unit(
unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
si_unit=@alt_siunit,
value=@altitude,
unit=@alt_unit_type)/
%^loc_alt = $representing_value_with_unit.value%
Global_location_representation.altitude ->
^loc_alt
-- assign an identifier to the representation /
assigning_identification_with_no_organization(
items=Global_location_representation,
id=@geo_area,
id_class_name='Geographic_location_identification_code',
id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
-- end.
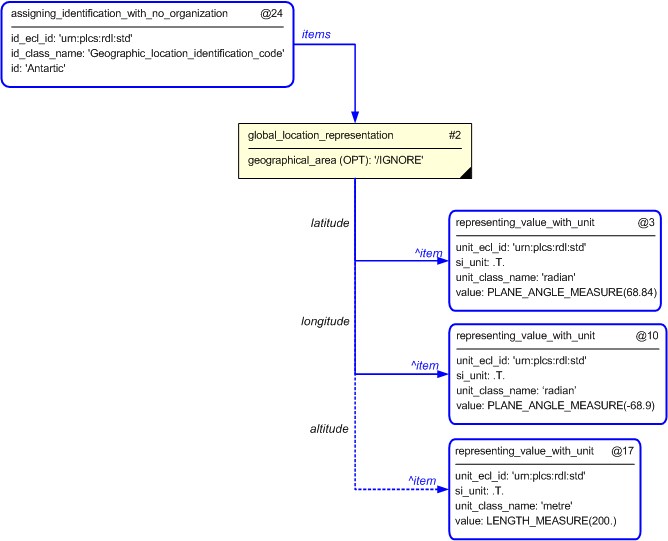
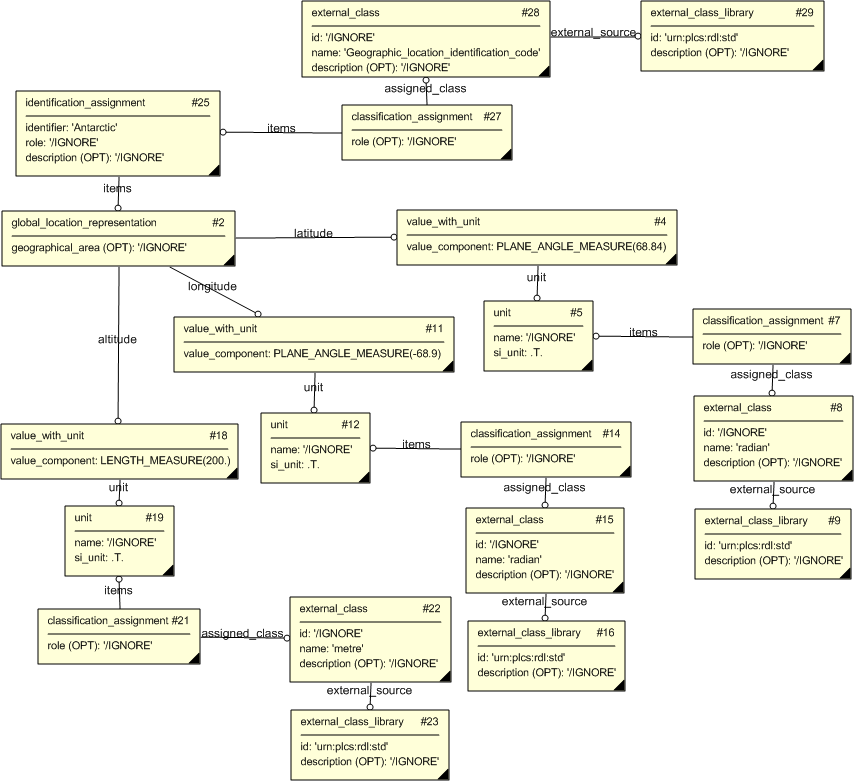
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
(an illustration of the consolidated template is shown in
Figure
7 below.)
Note that the templates
assigning_identification_with_no_organization and
representing_value_with_unit
are used in the diagram.
Namely:
@30 /assigning_identification_with_no_organization(id_class_name='Geographic_location_identification_code ', id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', id='Antarctic')/
and:
@3 /representing_value_with_unit(unit='radian', unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', si_unit='.T.', value='PLANE_ANGLE_MEASURE(68.84)')/
and:
@10 /representing_value_with_unit(unit='radian', unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', si_unit='.T.', value='PLANE_ANGLE_MEASURE(-68.9)')/
and:
@17 /representing_value_with_unit(unit='metre', unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', si_unit='.T.', value='LENGTH_MEASURE(200.0)')/
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by representing_geographical_location
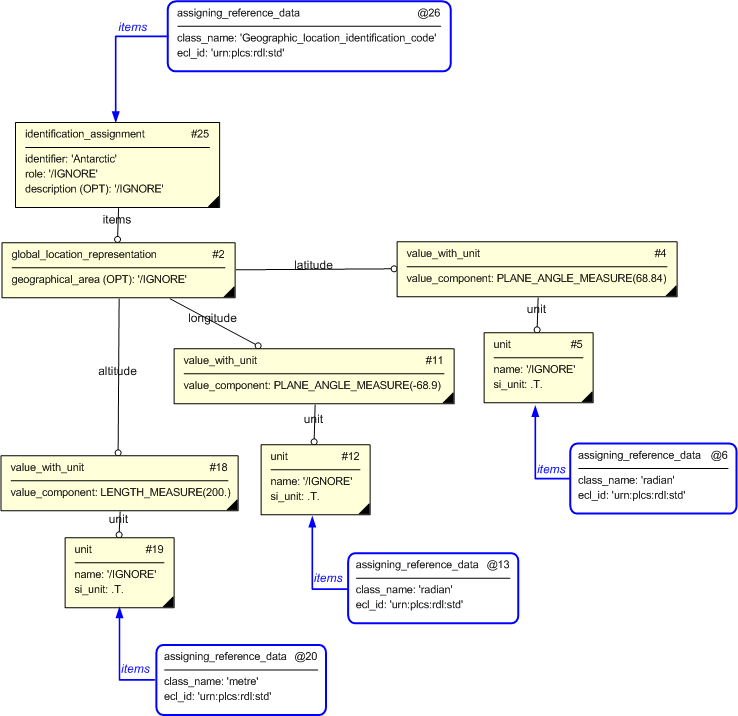
The instance diagram in Figure
5
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_geographical_location(lat_siunit='.T.', long_siunit='.T.', alt_siunit='.T.', lat_unit_type='radian', long_unit_type='radian', latitude='68.84', longitude='-68.9', alt_unit_type='metre', altitude='200.', geo_area='Antarctic')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_geographical_location template is shown in
Figure
7 below.)
Note that after expansion of the templates above and subsequent instance population, the following base
templates are used in the figure;
assigning_reference_data
Namely:
@6 /assigning_reference_data(class_name='radian', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
and:
@13 /assigning_reference_data(class_name='radian', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
and:
@20 /assigning_reference_data(class_name='metre', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
and:
@26 /assigning_reference_data(class_name='Geographic_location_identification_code ', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
.
Figure 5 — Entities instantiated by expanding representing_geographical_location
The instance diagram in Figure
6
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_geographical_location(lat_siunit='.T.', long_siunit='.T.', alt_siunit='.T.', lat_unit_type='radian', long_unit_type='radian', latitude='68.84', longitude='-68.9', alt_unit_type='metre', altitude='200.', geo_area='Antarctic')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_geographical_location template is shown in
Figure
7 below.)
Note that after expansion of all the templates above the subsequent instance population is shown in the
figure below.
Figure 6 — Entities instantiated by expanding representing_geographical_location
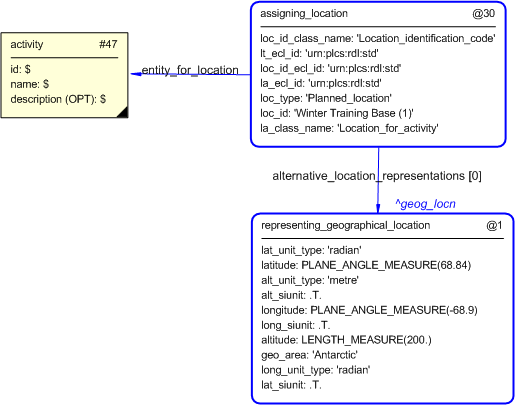
The instance diagram in
Figure
7
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_geographical_location(lat_siunit='.T.', long_siunit='.T.', alt_siunit='.T.', lat_unit_type='radian', long_unit_type='radian', latitude='68.84', longitude='-68.9', alt_unit_type='metre', altitude='200.', geo_area='Antarctic')/
Figure 7 — Instantiation of template
The following section details how the
representing_geographical_location
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Global_location_representation
NOTE this characterization is optional.