Capability:assigning_reference_data
Revision: 1.16
| Template:— assigning_business_specific_reference_data (asg_bs_rd) Capability:assigning_reference_data |
Date: 2009/04/09 14:00:39 Revision: 1.16 |
The use of template,assigning_business_specific_reference_data, has been deprecated since 2007-04-23.
Use assigning_reference_data instead.This section specifies the template assigning_business_specific_reference_data.
NOTE The template has been defined in the context of the capability assigning_reference_data which provides an overall description of the relevant parts of the ISO 10303-239 information model and a description of related templates.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
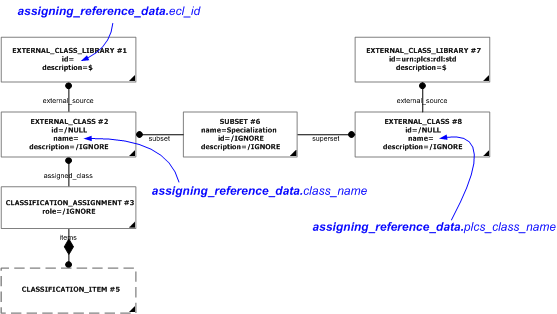
This template describes the classification of something as being a member of a class in a given business specific reference data library. The template supports the recommended approach in doing this, namely that a reference is provided for that business specific class back to the leaf superclass in the plcs reference data library.
This template illustrates the recommended approach for exchanging classifications done, based on business specific reference data libraries.
This template is based on the same assumptions as the template assigning_reference_data, namely that:

target
is the parameter to which the
External_class
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Classification_assignment.role | '/IGNORE' | — |
| External_class.id | '/IGNORE' | Class.id |
| External_class.description | '/IGNORE' | Class.description |
| External_class.name | @class_name | Class.name |
| External_class_library.id | @ecl_id | — |
| Subset.name | 'Specialization' | — |
| Subset.id | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Subset.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
| External_class.id | '/IGNORE' | Class.id |
| External_class.description | '/IGNORE' | Class.description |
| External_class.name | @plcs_class_name | Class.name |
| External_class_library.id | 'urn:plcs:rdl:std' | — |
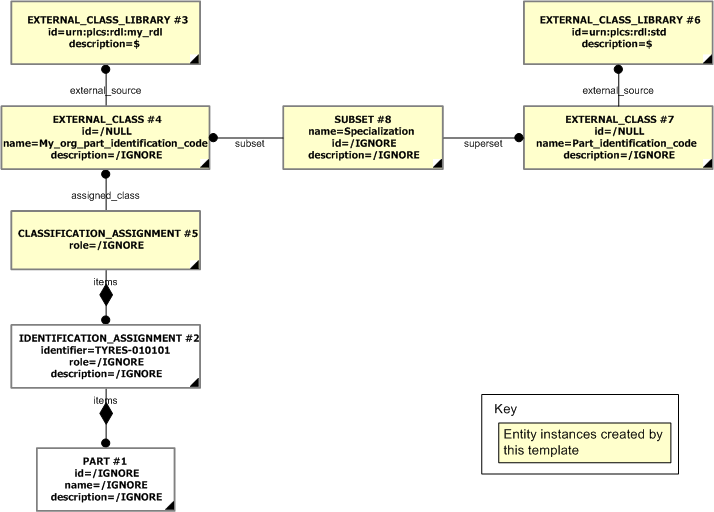
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part 28 ed.2 syntax) is:#1=PART('/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE'); #2=IDENTIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT('TYRES-010101', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', (#1)); #3=EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:my_rdl', '$'); #4=EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL', 'My_org_part_identification_code', '/IGNORE', #3); #5=CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4, (#2), '/IGNORE'); #6=EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:std', '$'); #7=EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL', 'Part_identification_code', '/IGNORE', #6); #8=SUBSET('/IGNORE', 'Specialization', '/IGNORE', #4, #7);;
© OASIS 2010 — All rights reserved