| Capability (C010):— assigning_reference_data | Date: 2007/06/22 12:22:09 Revision: 1.23 |
This section provides a business level overview of this capability.
Reference data are terms and definitions that have to be mutually understood by all parties involved in an information exchange.
Reference data are used to extend and to tailor the data model to meet the requirements of different groups of users and provide greater precision.
EXAMPLE There are many different types of document used in product life cycle support. The data model provides a basic capability for representing documents but does not specify the list of types of documents. Instead, the types of document are defined as reference data. The names and the corresponding definitions of the types of document could be stored in a RDL and then be referenced by all parties in the exchange.
This capability would be used to classify a document as a Maintenance Manual.
This section provides an overview of the information model that supports this capability.
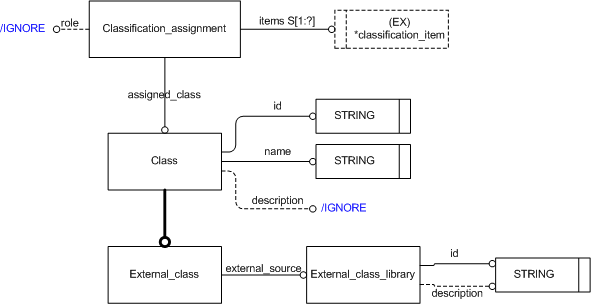
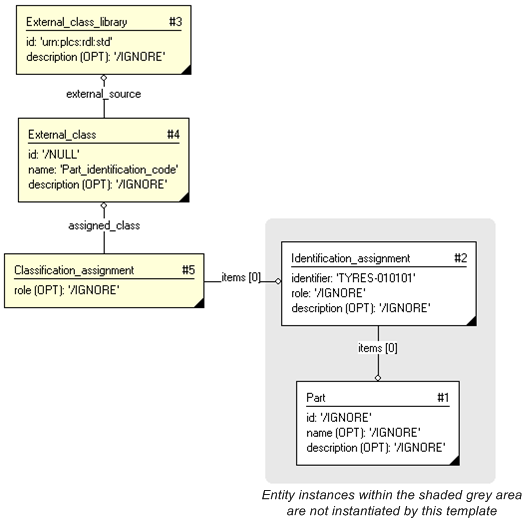
Reference data is applied using the Classification assignment and External class modules. The main entities used by this capability are shown in figure 1 below.

The reference data being applied are defined in external sources such as databases, web-sites, published documents etc. The source used for a particular instance of reference data shall be stated in the id attribute of the External_class_library entity. The identification may be a URN, URL, Document identification or any other identification that uniquely identifies the source. A complementary decription of the source may be provided using the External_class_library description attribute.
The reference data being applied shall be stated by name using External_class and its inhereted attribute name. In situations where a reference data class is uniquely identified by code, number, URN etc, rather than by name, the id attribute of External_class should hold the value of the identified class in the external class library.
The relationship between the reference data and the entity being described/classified is established using Classification_assignment.
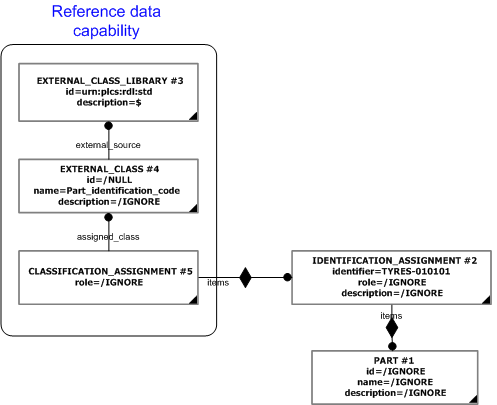
In the example above the identifier "TYRES-010101" is classified as being a "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) as defined in the PLCS standard reference data library (RDL) available on the the web via the URN "urn:plcs:rdl:std".
This section specifies how the information model can be further characterized by the assignment of additional information such as dates, approvals and people or organizations.
The following characterizations may apply.
This capability does not require any further characterization of the introduced entities. However, there is a requirement for decribing how to exchange information on reference data class hierarchies (superclasses).
The PLCS reference data has been designed to be extensible. A set of base classes are provided and these can be extended by organizations or industry to fit particular business needs. The extension is done by creating subclasses of the base classes and storing these in a business specific reference data library (RDL).
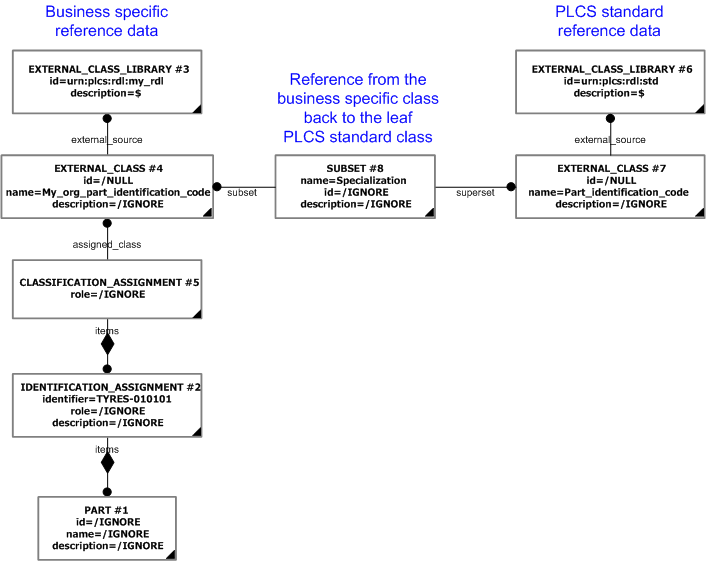
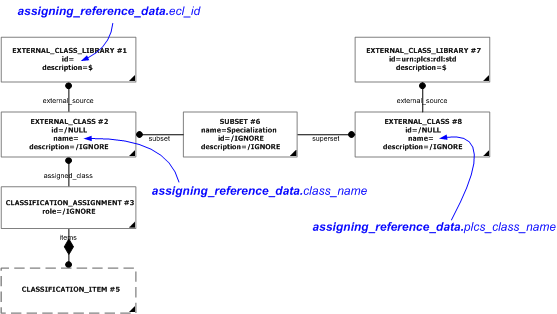
For example, a Part must have at least one identifier assigned (Identification_assignment) that is classified as a "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) in order to represent the part number. The class "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) is defined within the PLCS reference data library. However, an organization may specify their own encoding system for parts, so that they can identify parts with their own identifiers (i.e. an organization specific part identification code). For example, an organization may create a class "My_org_part_identification_code" for this purpose. This class is then a subclass of "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) (or subclass thereof). This is illustrated below.

A system reading a PLCS data exchange file that contains parts identified by "My_org_part_identification_code" may need to deduce that these are in fact "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code)s. To correctly read the file the system therefore has to have access to the class hierarchy information stored in a business specific RDL. However, it may be the case that a system reading a file does not have access to this business specific RDL containing the definition of the business specific class and its relationship to the PLCS classes.
To allow for this, whenever non standard reference data is used, i.e. reference data that has not been registered as part of the PLCS reference data, the non standard class shall be defined as a specialization of the first (leaf) PLCS class extended in the PLCS RDL. In this case, the class "My_org_part_identification_code" shall be defined as being a specialization of "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code).
The class hierarchy is represented using Subset, where superclass is represented as the External_class being subject of the superset attribute, and the subclass is represented as the External_class being subject of the subset attribute.
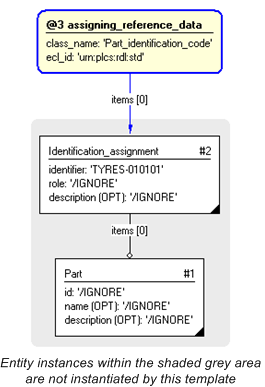
The instance diagram below shows the assignment of business specific reference data, "My_org_part_identification_code" identifier to a part, and at the same time providing a reference back to the leaf superclass defined within the standard PLCS reference data library.
This section describes additional usage guidance where the PLCS data model provides abilities closely related to the scope covered by this capability.
Do not use Qualified_property_value_representation
Use Assigned_property, Activity_property or Resource_property together with Classification_assignment.
Never use the role attribute for any entity.
Role attributes should be left empty. Role information should be defined using Classification_assignment.
There is also a module Attribute classification defined within the PDM modules that can be used for classification. The module is provided for backwards compatibility with the PDM Schema(http://www.pdm-if.org/). However, this module shall not be used.
In cases where classification is expected but the sending application does not contain the information on
how to classfy, this shall be resolved by the usage of the PLCS standard class
[Unknown]![]() Error RDL1: The class Unknown does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class Unknown does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The following sections define a set of templates for the capability, where a template is a specification of a set of entities that need to be instantiated to represent a given set of information.
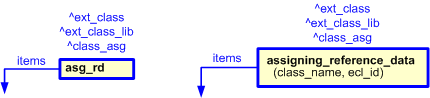
This section specifies the template assigning_reference_data.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
This template describes the classification of something as being a member of a class, where the definition of that class is defined in a given external Reference Data Library (RDL).
This template illustrates the most simplified assignment of reference data, where:
NOTE There is also a template for assigning codes for classification to entity instances in a data set (assigning_code). The usage of the assigning_code template applies when the assigned code isn't defined as a class within a Reference Data Library.
NOTE For DEXlib edition 1, this template is also used for representing 'Same_as' associations between entity instances in a data set and individuals in a Reference Data Library. 'Same_as' means that an entity instance in a data set represents the same thing as the individual defined in the RDL. The use of this template for 'Same_as' associations will be superseded in DEXlib edition 2 by the use of the new 'Same_as_identification' entity and its associated template.
NOTE For DEXlib edition 1, the External_class.name attribute is populated with the name of the class being referenced in an RDL, and the External_class_library.id attribute identifies the RDL where this class is defined. This will be superseded in DEXlib edition 2, where the External_class.id attribute will be populated with the full HTTP URN identifying the source where the class is defined (RDL and class name), and the External_class_library.id attribute will identify the context onthology for an actual data exchange.
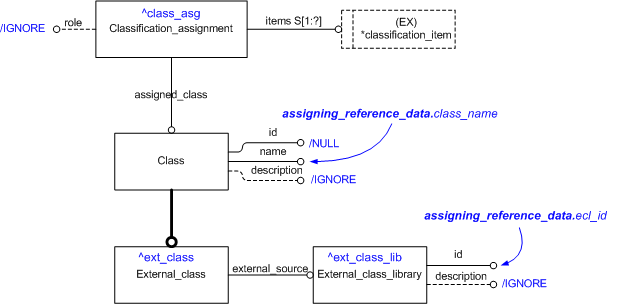
target
is the parameter to which the
External_class
is bound.
target
is the parameter to which the
External_class_library
is bound.
target
is the parameter to which the
Classification_assignment
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Classification_assignment.role | '/IGNORE' | — |
| External_class.id | '/NULL' | Class.id |
| External_class.description | '/IGNORE' | Class.description |
| External_class.name | @class_name | Class.name |
| External_class_library.id | @ecl_id | — |
| External_class_library.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
#1=PART('/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE'); #2=IDENTIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT('TYRES-010101', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', (#1)); #3=EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:std', '$'); #4=EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL', 'Part_identification_code', '/IGNORE', #3); #5=CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4, (#2), '/IGNORE');
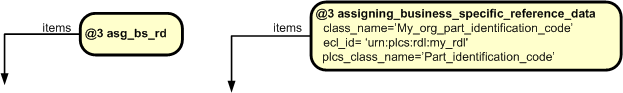
This section specifies the template assigning_business_specific_reference_data.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
The use of template,assigning_business_specific_reference_data, has been deprecated since 2007-04-23.
Use assigning_reference_data instead.This template describes the classification of something as being a member of a class in a given business specific reference data library. The template supports the recommended approach in doing this, namely that a reference is provided for that business specific class back to the leaf superclass in the plcs reference data library.
This template illustrates the recommended approach for exchanging classifications done, based on business specific reference data libraries.
This template is based on the same assumptions as the template assigning_reference_data, namely that:

target
is the parameter to which the
External_class
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Classification_assignment.role | '/IGNORE' | — |
| External_class.id | '/IGNORE' | Class.id |
| External_class.description | '/IGNORE' | Class.description |
| External_class.name | @class_name | Class.name |
| External_class_library.id | @ecl_id | — |
| Subset.name | 'Specialization' | — |
| Subset.id | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Subset.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
| External_class.id | '/IGNORE' | Class.id |
| External_class.description | '/IGNORE' | Class.description |
| External_class.name | @plcs_class_name | Class.name |
| External_class_library.id | 'urn:plcs:rdl:std' | — |
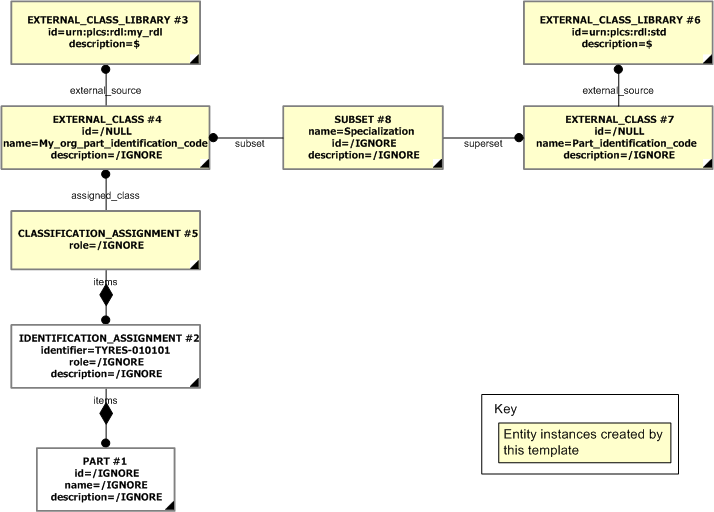
The instance model in STEP XML exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part 28 ed.2 syntax) is:#1=PART('/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE'); #2=IDENTIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT('TYRES-010101', '/IGNORE', '/IGNORE', (#1)); #3=EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:my_rdl', '$'); #4=EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL', 'My_org_part_identification_code', '/IGNORE', #3); #5=CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#4, (#2), '/IGNORE'); #6=EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:std', '$'); #7=EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL', 'Part_identification_code', '/IGNORE', #6); #8=SUBSET('/IGNORE', 'Specialization', '/IGNORE', #4, #7);;
This capability "Applying classification through the use of reference data" is related to the following capabilities:
Other ISO standards that defines classes that can be used in information exchanges are:
ISO 15926 includes standardization of the data associated with the engineering construction and operation of oil and gas production facilities. The scope of activities to be supported by this standard includes:
For more information visit Official ISO TC184/SC4 Web Site(http://www.tc184-sc4.org).
ISO 13584 is a series of International Standards for the computer-sensible representation and exchange of part library data. The objective is to provide a mechanism capable of transferring parts library data, independent of any application which is using a parts library data system. The nature of this description makes it suitable not only for the exchange of files containing parts, but also as a basis for implementing and sharing databases of parts library data.
For more information visit Official ISO TC184/SC4 Web Site(http://www.tc184-sc4.org).
© OASIS 2010 — All rights reserved