Template:— property (prop)
Context:— UK_Defence |
Date: 2010/03/16 16:51:20
Revision: 1.9
|
This section specifies the template property.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of
UK_Defence.
Refer to the business context for details of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent the UK_Defence concept of a property
in terms of PLCS model elements (templates, entities, and reference data).
The property business object is used by those UK_Defence Data Exchange
Specifications that require information about a functional or physical aspect of the information object that it is
a property of.
Figure 1 — Graphical Representation for Business Object Property
Property:
The definition of a property object is:
This information object represents a property that defines a functional or physical aspect of the information object
that it is a property of.
Typical properties of Physical Designs are:
- Length, Width, Height (Envelope dimensions).
- Unladen and Laden Weight.
- Minimum and Maximum operating temperatures, pressures, humidities, heights.
Typical properties of Products would mirror those of its Physical Design.
|
Attribute name
|
Attribute description
|
Attribute type
|
Optionality
|
| A property of |
This is the reference to the thing for which this property is created
NOTE
There is currently no-map for the select relationship to product_usage_feedback.
This has been raised as an issue against the AP239 schema.
|
SELECT |
Mandatory |
| Category |
This is the category of the property.
EXAMPLE
(From EandAM ICD):
- sortie life property
- sortie feedback property
|
intrinsic |
Optional |
| Disposition |
This is the disposition of the property, ie whether the property is:
- estimated
- predicted
- designed
- measured/actual
|
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| ID |
This is the identifier of the Property. This would typically contain a human interpretable name. |
Identifier |
Mandatory |
| Unit |
This is the unit of the Property. This is typically:
- an SI unit,
- an Imperial Unit,
- any other accepted or standard denomination of quantity (such as currency units),
- any equipment specific usage unit.
|
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| Valid from |
This is the date and time from which the property was valid. |
intrinsic |
Optional |
| Valid to |
This is the date and time from which the property was valid. |
intrinsic |
Optional |
| Value |
This is the value of the property. |
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
Table 1 — Property attribute details
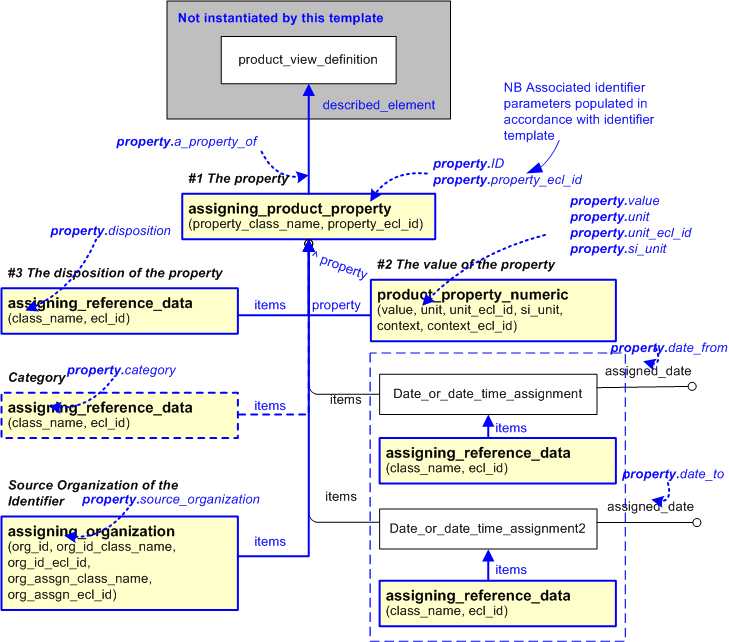
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"property".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 2 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for property
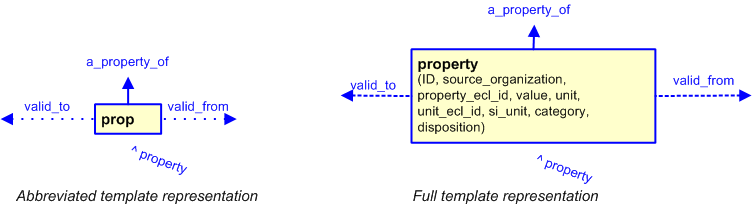
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
Figure 3 — The graphical representation of the property template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The identifier of the Property.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Property]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Quantified_property]
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml[Quantified_property]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
The organization that created the associated identifier. Additionally
a Person or Information System could be defined when either of these are the source; see Identifier template characterizations
The identifier of the
External_class_library
storing the definition of the class referenced by the parameter @property_identifier.
The value of the property.
The data type must also be indicated in this parameter, e.g.
"ANY_NUMBER_VALUE(5)".
The class name of the unit in which the value is expressed.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The identifier of the
External_class_library
storing the definition of the class referenced by the parameter @property_unit.
Value should be set to true if the unit is a SI base unit defined by ISO, i.e.
kilogram (kg) for Mass,
second (s) for Time,
metre (m) for Displacement,
ampere (A) for Electrical current,
kelvin (K) for Temperature,
mole (mol) for Amount of substance, and
candela (cd) for Luminous intensity. If this is not the case it should be set to false.
Note that the representation of true and false depends on exchange format. In Part 11 (a STEP file) true is
represented by the string ".T.", and false by ".F.", while in Part 28 (XML) they are represented by text strings
"true"
and "false".
The category of the property.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Property_category]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
The disposition of the Property.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
classifications: [Disposition]![[warning:]](../../../../../../images/dex/warning.gif) Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL4: The URI urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence is not listed in dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
The view of the object to which the property is assigned
This is the date and time from which the property was valid.
This is the date and time from which the property was valid.
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Assigned_property
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $property.property%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Property
Each instance of the
entity
(
Assigned_property)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (property) namely:
a_property_of,
ID.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
property.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
-- Property ID and A property of /
assigning_product_property(
property_class_name=@ID,
property_ecl_id=@property_ecl_id,
described_element=@a_property_of)/
-- Assign reference parameter %^property = $assigning_product_property.property%
-- Assign source_organization /
assigning_organization(
org_id=@source_organization,
org_id_class_name='Organization_name',
org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
org_assgn_class_name='Source_organization',
org_assgn_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
items=^property)/
-- Value and Unit /
product_property_numeric(
value=@value,
unit=@unit,
unit_ecl_id=@unit_ecl_id,
si_unit=@si_unit,
context='Numerical_representation_context',
context_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
property=^property)/
-- [ optional Category] /
assigning_reference_data(
class_name=@category,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
items=^property)/
-- Disposition /
assigning_reference_data(
class_name=@disposition,
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
items=^property)/
-- [ optional valid from date] Date_or_date_time_assignment%^valid_from_date =
Date_or_date_time_assignment%
^valid_from_date.assigned_date ->
@valid_from
^valid_from_date.role = 'property_valid_from'
^valid_from_date.items ->
^property
/
assigning_reference_data(
items=^valid_from_date,
class_name='Date_valid_from',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- [ optional valid to date] Date_or_date_time_assignment%^valid_to_date =
Date_or_date_time_assignment%
^valid_to_date.assigned_date ->
@valid_to
^valid_to_date.role = 'property_valid_to'
^valid_to_date.items ->
^property
/
assigning_reference_data(
items=^valid_to_date,
class_name='Date_valid_to',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
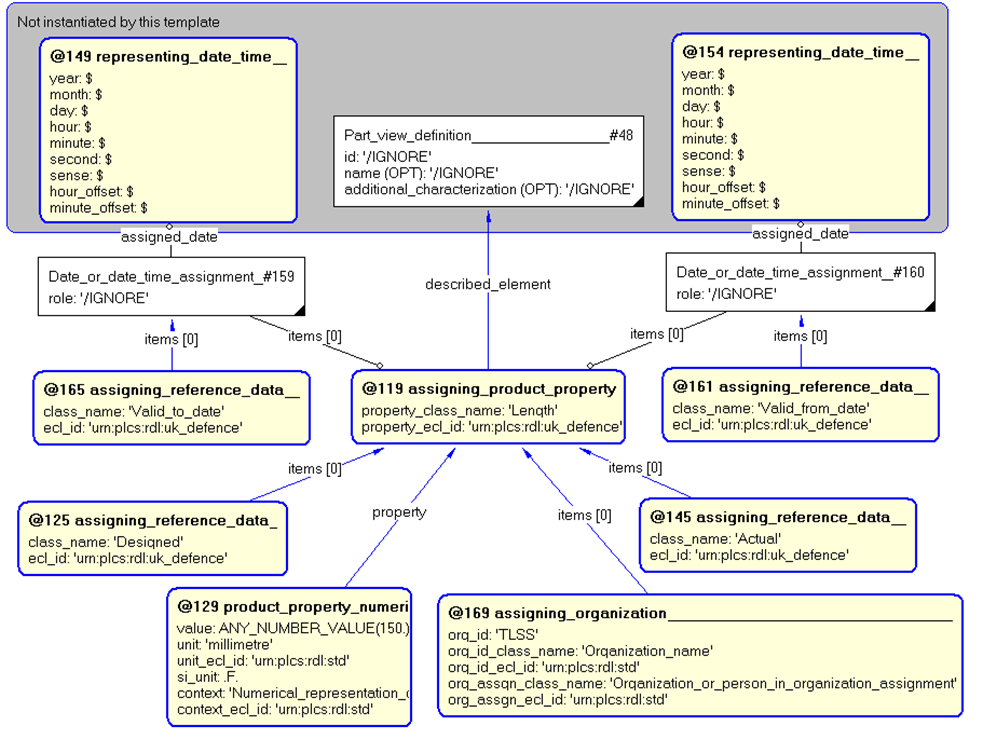
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/property(ID='Length', source_organization='TLSS', property_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence', value='ANY_NUMBER_VALUE(150.)', unit='millimetre', unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', si_unit='.F.', category='Actual', disposition='Designed', a_property_of='#48', valid_from='#154', valid_to='#149')/
(an illustration of the consolidated property template is shown in
Figure
5 below.)
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by property template
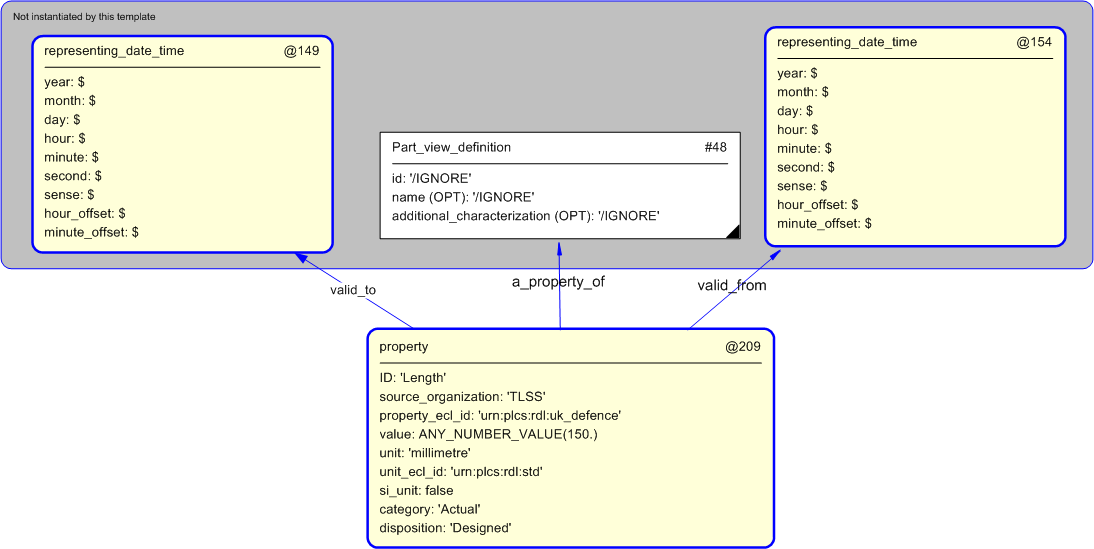
The instance diagram in
Figure
5
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/property(ID='Length', source_organization='TLSS', property_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence', value='ANY_NUMBER_VALUE(150.)', unit='millimetre', unit_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', si_unit='.F.', category='Actual', disposition='Designed', a_property_of='#48', valid_from='#154', valid_to='#149')/
Figure 5 — Instantiation of property template
Characterizations
No common characterizations of the template
property
have been identified. However, the ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model
may enable other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.