Template:— configuration_item (cnfg_itm)
Context:— UK_Defence |
Date: 2009/04/17 10:46:56
Revision: 1.4
|
This section specifies the template configuration_item.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of
UK_Defence.
Refer to the business context for details of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes the identification of, and the reference to, an item that has been designated for Configuration Management.
The configuration_item business object is used by those UK_Defence data Exchange Specifications that require configuration
information.
This information object represents the identification of, and the reference to, an item that is subject to formal Configuration
Management processes throughout its life.
Note - Criteria for selection of configuration_item shall include, but not be limited to:
- a) Safety;
- b) Criticality and complexity;
- c) Costs and purchasing;
- d) Functionality and performance;
- e) Integration, interchangeability and status as a replaceable item;
- f) Integrated Logistic Support (ILS);
- g) Reliability and maintainability;
- h) Organization, management and responsibility considerations.
The configuration_item is often associated with the issue level information of the production build.
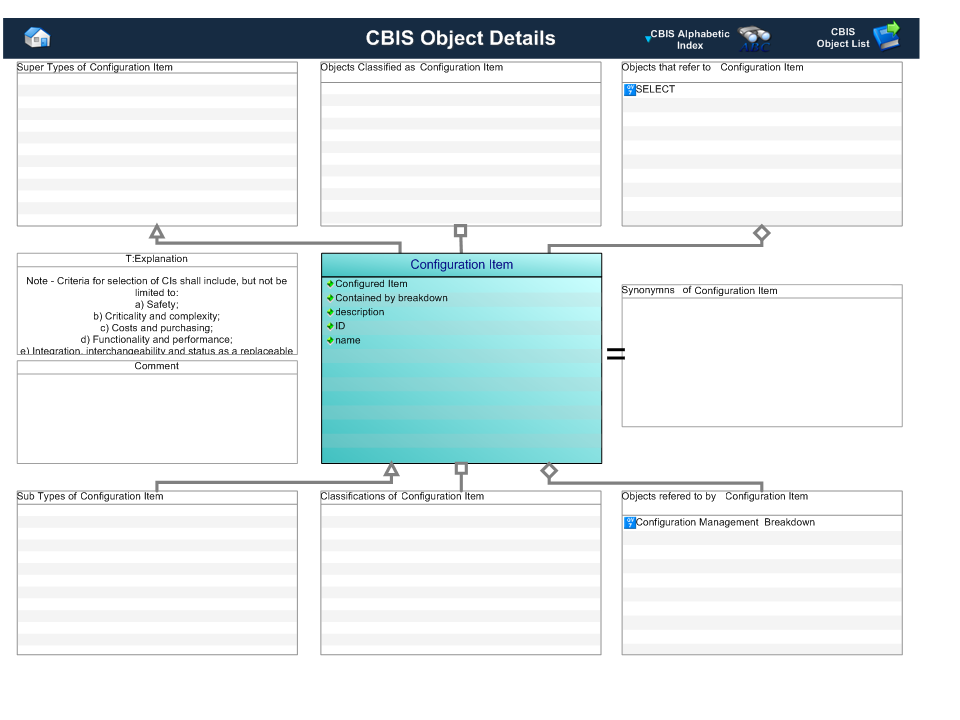
Figure 1 — Graphical Representation for Business Object Configuration Item
This information object represents the configuration for an applicable item.
|
Attribute name
|
Attribute description
|
Attribute type
|
Optionality
|
| Configured Item |
This is the reference to the item that has been identified as being necessary to control through formal configuration management
processes.
|
SELECT |
Mandatory |
| description |
This attribute provides the description of the Item. |
Intrinsic |
Optional |
| ID |
This is the identifier of the configuration item. This may just be a copy of the identifier of the referenced item, but in
some circumstances, additional identifiers may be assigned - for example, the addition of Configuration Management Numbers
or Physical Logistic Analysis Control Numbers to items that have already been defined in a Physical Design Breakdown.
|
Identifier |
Mandatory |
| Identifier.id |
This is the value of the id attribute of the Identifier applied to the Configuration Item. |
intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| Identifier.type |
This attribute is the type associated with the id of the Identifier given to the Configuration Item. This must be one of the
classes provided.
|
CMN or LCN |
Mandatory |
| Identifier.source_organization |
This attribute is the value representing the source organization that provides the id of the Identifier given to the Configuration
Item. This value is assumed to be a type of Organization_identification_code.
|
Organization_identification_code |
Mandatory |
| name |
This attribute provides the name of the Configuration Item. |
Intrinsic |
Mandatory |
| contained_by_breakdown |
This attribute provides the relationship to the configuration that the Configuration Item is defined for. |
Relationship to Configuration Management Breakdown |
Mandatory |
Table 1 — Configuration Item attribute details
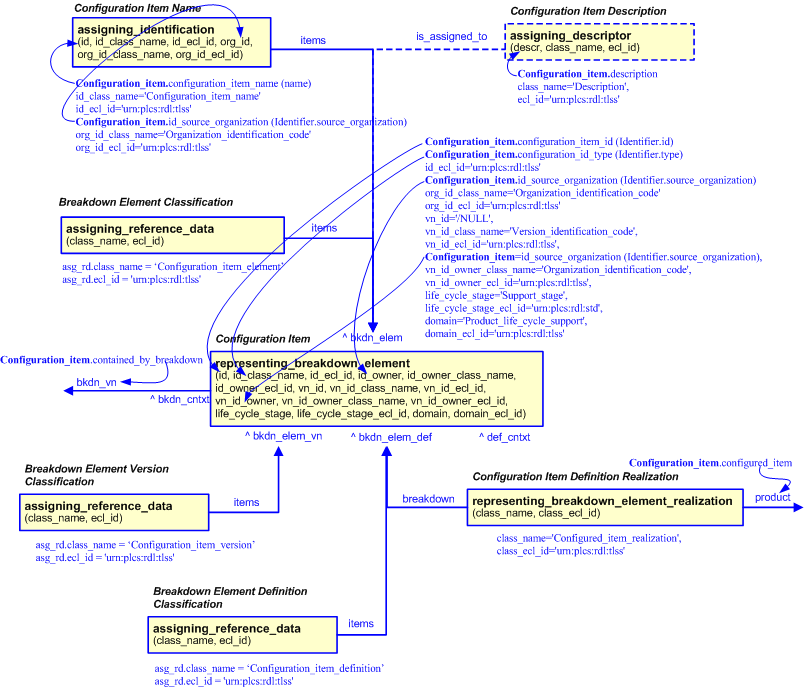
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
2
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"configuration_item".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
The configuration item template is based upon the representing_breakdown_element template. Since there is no in-built PLCS
breakdown element type for configuration item, it is necesary to classify those entities to allow systems to distinguish between
elements used as configuration items and those used for other purposes. Hence, the breakdown_element, breakdown_element_version
and breakdown_element_definition are classified using appropriate reference data. The configuration item (breakdown element
definition) is an element of (contained_by_breakdown) a breakdown version (out of scope). This template also assumes that
a configuration item (breakdown element definition) has a configured item that realizes it. The configured item is out of
scope of this template.
Figure 2 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for configuration_item
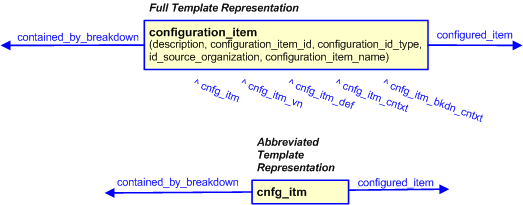
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
3
below.
The resulting configuration item template is shown below.
Figure 3 — The graphical representation of the configuration_item template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
This is the reference to the item that has been identified as being necessary to control through formal configuration
management processes.
This attribute provides the description of the Item.
This is the identifier of the Configuration Item.
This may just be a copy of the identifier of the referenced item, but in some circumstances, additional identifiers may be
assigned - for example, the addition of Configuration Management Numbers or Physical Logistic Analysis Control Numbers to
items that have already been defined in a Physical Design Breakdown.
This attribute is provides the type associated with the id of the Identifier given to the Configuration Item. This
must be one of the classes provided.
The identifier of the organization that owns the Configuration item id. It is assumed that this will be of type Orgainzation_identification_code
and not an Organization name.
This attribute provides the name of the configured item.
The breakdown version that contains this element.
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Breakdown_element
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $configuration_item.cnfg_itm%
%^target = $configuration_item.cnfg_itm_vn%
%^target = $configuration_item.cnfg_itm_def%
%^target = $configuration_item.cnfg_itm_cntxt%
Allow the
Breakdown_context
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $configuration_item.cnfg_itm_bkdn_cntxt%
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
/
representing_breakdown_element(
id=@configuration_item_id,
id_class_name=@configuration_id_type,
id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
id_owner=@id_source_organization,
id_owner_class_name='Organization_identification_code',
id_owner_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
vn_id='/Null',
vn_id_class_name='Version_identification_code',
vn_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
vn_id_owner=@id_source_organization,
vn_id_owner_class_name='Organization_identification_code',
vn_id_owner_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
life_cycle_stage='Support_stage',
life_cycle_stage_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
domain='Product_life_cycle_support',
domain_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- re-direct the output from the call.. %^cnfg_itm = $representing_breakdown_element.bkdn_elem%
%^cnfg_itm_vn = $representing_breakdown_element.bkdn_elem_vn%
%^cnfg_itm_def = $representing_breakdown_element.bkdn_elem_def%
%^cnfg_itm_cntxt = $representing_breakdown_element.def_cntxt%
%^cnfg_itm_bkdn_cntxt = $representing_breakdown_element.bkdn_cntxt%
^cnfg_itm_bkdn_cntxt.breakdown ->
@contained_by_breakdown/
assigning_descriptor(
descr=@description,
class_name='Description',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
is_assigned_to=^cnfg_itm)/
/
representing_breakdown_element_realization(
breakdown=^cnfg_itm_def,
product=@configured_item,
class_name='configuration_item_realization',
class_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
-- assign name to breakdown_element /
assigning_identification(
id=@configuration_item_name,
id_class_name='configuration_item_name',
id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
org_id=@id_source_organization,
org_id_class_name='Organization_identification_code',
org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence',
items=^cnfg_itm)/
-- provide the role of the identification by classifying the Identification_assignment /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^cnfg_itm,
class_name='configuration_item_element',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
/
assigning_reference_data(
items=^cnfg_itm_vn,
class_name='configuration_item_version',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
/
assigning_reference_data(
items=^cnfg_itm_def,
class_name='configuration_item_definition',
ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:uk_defence')/
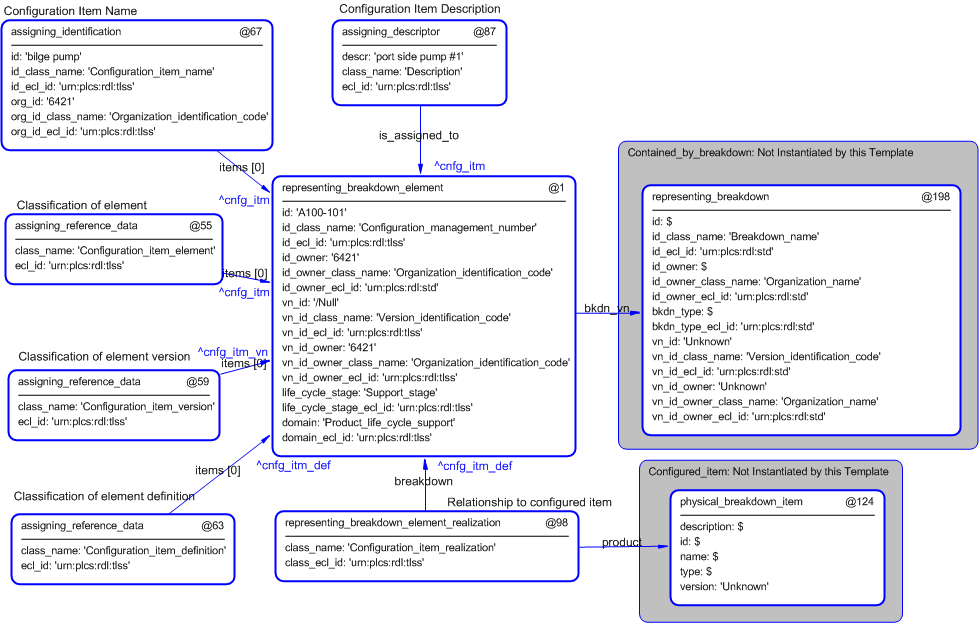
The instance diagram in Figure
4
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
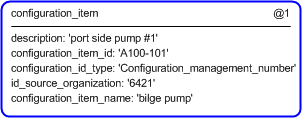
/configuration_item(description='port side pump #1', configuration_item_id='A100-101', configuration_id_type='Configuration_management_number', id_source_organization='6421', configuration_item_name='bilge pump')/
(an illustration of the consolidated configuration_item template is shown in
Figure
5 below.)
Figure 4 — Entities instantiated by configuration_item template
The instance diagram in
Figure
5
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/configuration_item(description='port side pump #1', configuration_item_id='A100-101', configuration_id_type='Configuration_management_number', id_source_organization='6421', configuration_item_name='bilge pump')/
Figure 5 — Instantiation of configuration_item template
The following section details how the
configuration_item
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in Figure
6
shows the possible characterizations of the template
"configuration_item".
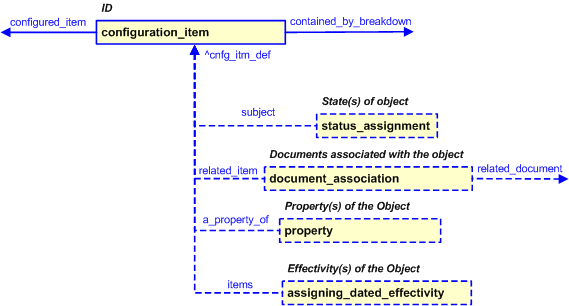
Figure 6 — Characterizations for configuration_item
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Property
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A UK_Defence.configuration_item
may have specific properties assigned to it, through the use of the following templates (or those based upon these):
UK_Defence.property. The following template calls show how these characterizations
might be instantiated.
/property(property_identifier='', property_ecl_id='', property_value='', property_unit='', unit_ecl_id='', si_unit='', disposition='', a_property_of='')/
Characterization Status Assignment
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A UK_Defence.configuration_item
may have one or more status assigned to it, through the use of the following templates (or those based upon these):
UK_Defence.status_assignment.
The following template calls show how these characterizations
might be instantiated.
/status_assignment(assigned_status='', assigned_status_ecl_id='', ID='', ID_type='', ID_organization='', subject='', type='', type_ecl_id='')/
Characterization Document Association
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A UK_Defence.configuration_item
may have specific documents assigned to it, through the use of the following templates (or those based upon these): UK_Defence.document_association
, and the associated UK_Defence.document
. The following template calls show how these characterizations
might be instantiated.
/document_association(id='', type='', source_organization='', purpose='', related_document='', related_item='')/
Characterization Assigning effectivity
NOTE this characterization is optional.