Template:— representing_state_type (rep_state_type)
Capability:representing_state_type |
Date: 2009/04/06 15:58:46
Revision: 1.6
|
This section specifies the template representing_state_type.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of the capability
representing_state_type
which provides an overall description of the
relevant parts of the ISO 10303-239 information model and a description
of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent state definitions.
State definitions define the types of states that can, or can be expected to, exist.
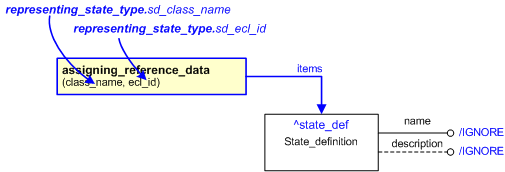
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_state_type".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_state_type
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_state_type template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The name of the class that defines the state type.
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
sd_ecl_id (Default=urn:plcs:rdl:std,Type='URN')
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
State_definition
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_state_type.state_def%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: State_definition
Each instance of the
entity
(
State_definition)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_state_type) namely:
sd_class_name,
sd_ecl_id.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
state_def.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
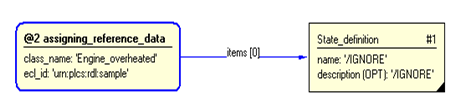
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_state_type(sd_class_name='Engine_overheated', sd_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_state_type template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_state_type template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#1 = STATE_DEFINITION('/IGNORE','/IGNORE');
#2 = EXTERNAL_CLASS_LIBRARY('urn:plcs:rdl:sample','/IGNORE');
#3 = EXTERNAL_CLASS('/NULL','Engine_overheated','/IGNORE',#2);
#4 = CLASSIFICATION_ASSIGNMENT(#3,(#1),'/IGNORE');
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_state_type(sd_class_name='Engine_overheated', sd_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_state_type template
Characterizations
No common characterizations of the template
representing_state_type
have been identified. However, the ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model
may enable other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.