Template:— representing_scheme_entry (rep_schm_entry)
Capability:representing_scheme |
Date: 2009/07/25 12:13:38
Revision: 1.1
|
This section specifies the template representing_scheme_entry.
NOTE
The template has been defined in the context of the capability
representing_scheme
which provides an overall description of the
relevant parts of the ISO 10303-239 information model and a description
of related templates.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a scheme entry,
and any assignments of activities, events, or task_metthods, etc. to it.
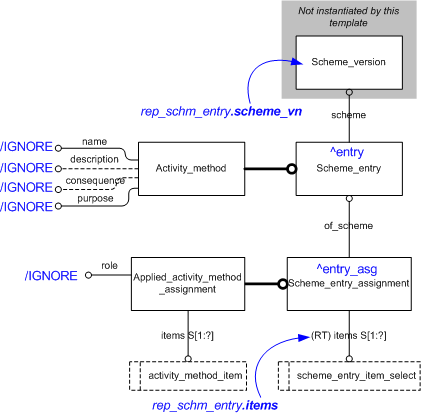
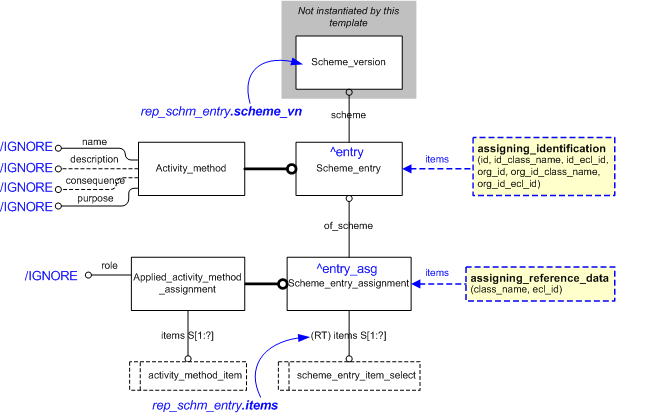
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_scheme_entry".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_scheme_entry
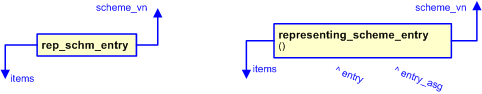
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_scheme_entry template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The items being assigned to the Scheme_entry, e.g. an activity.
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Scheme_entry
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Scheme_entry
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $representing_scheme_entry.entry%
where
target
is the parameter to which the
Scheme_entry
is bound.
%^target = $representing_scheme_entry.entry_asg%
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Scheme entry
Each instance of the
entities
(
Scheme_entry,
Scheme_entry_assignment)
within the data set shall be uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_scheme_entry) namely:
scheme_vn,
items.
The
instances are
referenced by the following template parameters:
entryentry_asg.
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
A description of templates and the syntax for the instantiation path is
provided in the
Templates Help/Information section.
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
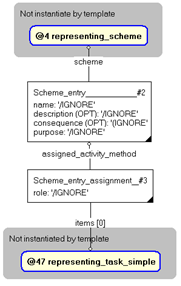
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_scheme_entry(scheme_vn='#26', items='#48')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_scheme_entry template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_scheme_entry template
The instance model in STEP ASCII exchange file format (ISO 10303 Part
21 syntax) is:
#2 = SCHEME_ENTRY('/IGNORE','/IGNORE','/IGNORE','/IGNORE',#26);
#3 = SCHEME_ENTRY_ASSIGNMENT(#2,(#48),'/IGNORE');
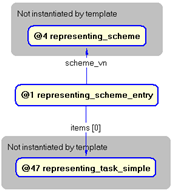
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_scheme_entry(scheme_vn='#26', items='#48')/
Figure 4 — Instantiation of representing_scheme_entry template
The following section details how the
representing_scheme_entry
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
The EXPRESS-G diagram in Figure
5
shows the possible characterizations of the template
"representing_scheme_entry".
Figure 5 — Characterizations for representing_scheme_entry
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning identification
NOTE this characterization is optional.
Characterization Assigning reference data
NOTE this characterization is optional.