 Issue:
RBN-1 by Rob Bodington (04-09-02) [minor_technical, closed] - {Type = contents}
Issue:
RBN-1 by Rob Bodington (04-09-02) [minor_technical, closed] - {Type = contents}The class "created" has been changed to "Date_created". The diagram needs to change
Comment: (Rob Bodington 04-09-29)
Changed
| Capability (C043):— representing_environment_typical | Date: 2007/07/11 16:32:00 Revision: 1.24 |
Issue: RBN-1 by Rob Bodington (04-09-02) [minor_technical, closed] - {Type = contents}
The class "created" has been changed to "Date_created". The diagram needs to changeComment: (Rob Bodington 04-09-29)
Changed
This capability describes how to represent a typical environment where an environment is the external physical conditions, such as average temperature, visibility, humidity etc.
The information required to represent a typical environment is summarized in the EXPRESS-G diagram in Figure 1 below and described in the following sections. The diagram also shows the relationship between a Product_as_realized and the environment to show how a Product_as_realized can be related to a typical environment.
NOTE The EXPRESS-G is not complete. For the complete EXPRESS see the modules: State observed, State definition and State characterized.
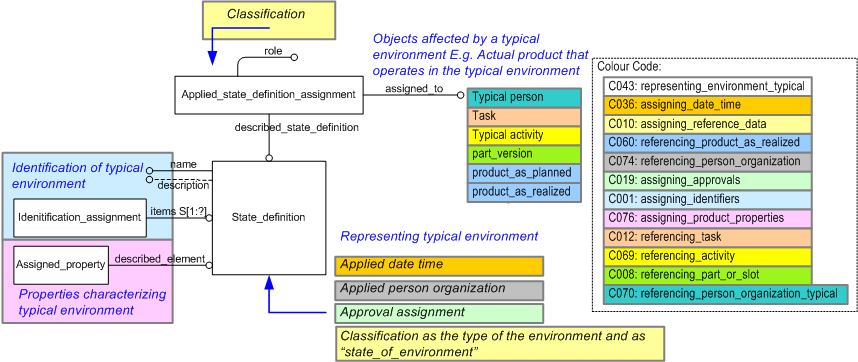
A typical environment is represented using the
State_definition
entity
(see C007: representing_state_type for details on
states) which is classified as
[State_of_environment]![]() Error RDL1: The class State_of_environment does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class State_of_environment does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
.
The typical environment, State_definition, is identified by using Identification_assignment to assign an identifier as described in C001: assigning_identifiers.
A set of properties are associated to the State_definition providing a definition of the typical environmental characteristics such as temperature and humidity that characterize the environment (see capability C076: assigning_product_properties for details on representing properties).
A typical environment can associated with a number of objects, such as people, tasks, activities, products indicating the typical environment that:
The Applied_state_definition_assignment relationship is used to associate the typical environment, State_definition to the object. The precise meaning of the relationship is specified by reference data applied to the relationship using Classification_assignment. Reference data is described in the capability: C010: assigning_reference_data.
For example, the fact that a given Product_as_individual (Either planned Product_as_planned or actual Product_as_realized) can operate in a given typical environment is represented by assigning the typical environment, State_definition, to the Product_as_individual by using the relationship Applied_state_definition_assignment.
Assigning a Person or Organization
The person or organization that defined the typical environment, State_definition, can be represented by assigning a Person_in_organization (using the relationship Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) to the typical environment, State_definition.
Similarly, the person or organization that identified that the Product_as_individual could operate in a typical environment, can be represented by assigning a Person_in_organization (using the relationship Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) to the Applied_state_definition_assignment that relates the typical environment, State_definition, to the Product_as_individual.
The Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment is classified as "Creator of" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Creator of).
NOTE The assignment of a person or organization is described in the capability C016: representing_person_organization.
The date when the typical environment was defined can be represented by the use of Date_or_date_time_assignments to assign a Date_time or Calendar_date to the typical environment, State_definition.
The Date_or_date_time_assignment is classified as "Date actual creation" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date actual creation).
NOTE The assignment of dates is described the capability C036: assigning_date_time.
Similarly, the date when it was identified that the Product_as_individual could operate in a typical environment, can be represented by assigning a Date_time or Calendar_date to the Applied_state_definition_assignment that relates the typical environment, State_definition, to the Product_as_individual.
The Date_or_date_time_assignment is classified as "Date actual creation" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date actual creation).
If documentation about the typical environment is required then
documents can be assigned to the typical environment
(State_definition)
using the
Document_assignment
relationship as described in capability
referencing_documents![]() Error C1: Capability referencing_documents not in dex_index.xml
Error C1: Capability referencing_documents not in dex_index.xml
.
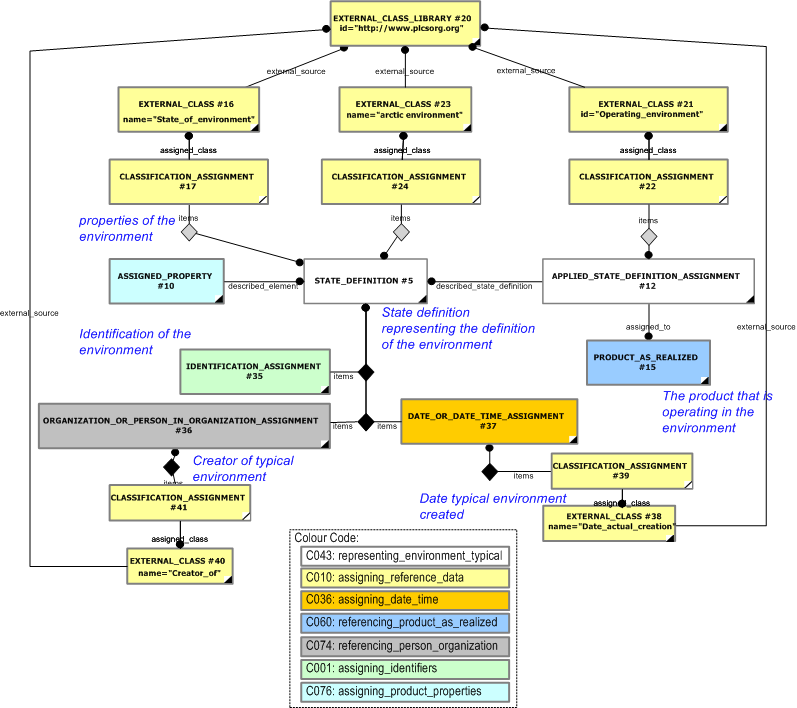
An example showing how a State_definition and assigned properties are used to represent an environment and a Product_as_realized operating in that environment is shown in Figure 2.
NOTE
The
State_definition
is classified as
[State_of_environment]![]() Error RDL1: The class State_of_environment does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
Error RDL1: The class State_of_environment does not exist in RDL at URI urn:plcs:rdl:std. Check the dexlib/data/refdata/rdl_index.xml
to indicate that it is a definition for an environment.
As an example
State_definition
has been further classified as an "Arctic_environment".
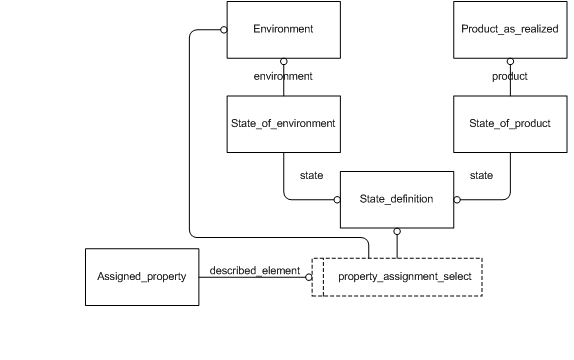
NOTE PLCS has not developed an explicit module for environment. If it had the model would be similar to the EXPRESS-G diagram shown in Figure 3, where an Environment is defined by a series of states, or in simpler cases, by a set of properties.
This capability "Representing a typical environment" is related to the following capabilities:
This capability "Representing a typical environment" is dependent on the following capabilities:
The following classes of reference data are required for this capability:
[State_of_environment]© OASIS 2010 — All rights reserved