| Capability (C001):— assigning_identifiers | Date: 2007/08/09 14:58:28 Revision: 1.52 |
This section provides a business level overview of this capability.
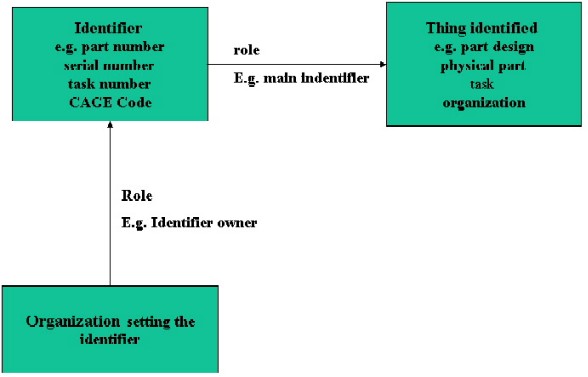
An Identification_assignment, is the assignment of an identifier to product or activity data. Such items are identified by creating an identifier that is unique in the context of an organization (or enterprise) and assigning the identifier to the item.
However, for many reasons (e.g. compatibility) the model specified within ISO 10303-239 has many entities that have a single "id" and or "name". This implies that there is only ever one identifier for an object unless over-written. Over time, however, objects may become associated with more than one identifier, such as an organization providing it's own identifier for parts supplied by another. For these identifiers to be useful, it is (as a minimum), necessary to know the organization that created or assigned the respective identifier. Typically the assigning organization, will ensure the uniqueness of the identifier. The identifier itself may be realized as a code, a name or a number.
EXAMPLE A DUNS code or a CAGE Code is an example of an identification that can be assigned to an organization.
EXAMPLE A Part Number is an example of an identification that can be assigned to the design of a Part.
EXAMPLE A Serial Number is an example of an identification that can be assigned to a physical instance of a Part (a Product_as_individual).
EXAMPLE A UID is an example as described in the DOD Memorandum "The Department of Defence Guide to Uniquely Identifying Items, Version 1.3" dated November 25th, 2003 (http://www.acq.osd.mil/uid).

Optionally, it may be appropriate to record the date and time when such an identifier was assigned.
Examples of Organizations that provide the context for an identifier include; Prime Contractor, Design Owner, MOD, Catalogue Owner.
To clarify the difference between codes used for identification and codes used as for classification purposes, we define codes as strings that are structured according to some convention. Often different sets of characters within the string carry a particular meaning. For example, part numbers are sometimes made up of a set of strings, with each set carrying some meaning. For example, product function, manufacturing plant etc. Structured codes are traditionally used for two purposes:
Where the code is being used for identification purposes, this capability (C001: assigning_identifiers), should be used.
C093: assigning_codes, should be used when a code is provided for classification or characterization purposes, and when the code is not available as a class within an existing reference data library (RDL) (see C010: assigning_reference_data).
This section provides an overview of the information model that supports this capability.
For the reasons stated in the business overview, a new approach to identification has been developed. The general approach of this is outlined and then detailed below.
PLCS allows a general approach to identification that comprises the following key assignments;
Firstly, the Identification_assignment entity both represents an identifier and makes the association of that identifier to one or more related items (for example, a Part), through the identification_item select type. This is the key function of this entity.
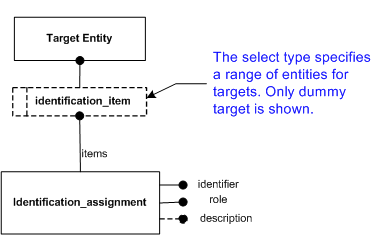
There should be one instance of Identification_assignment for each distinct identifier value that is required. Note, the model does not allow for identifiers to be maintained without an associated item.
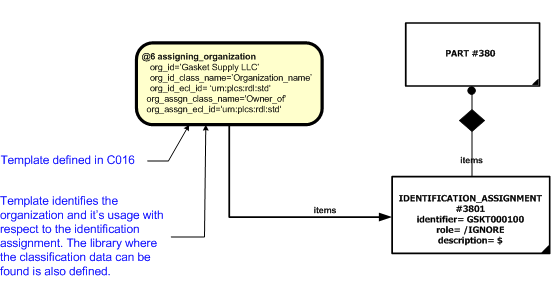
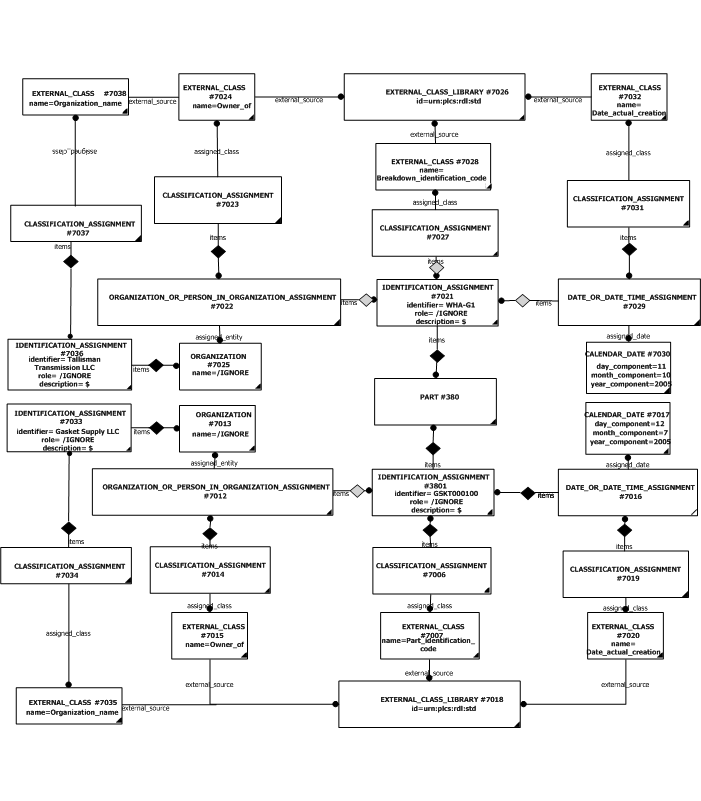
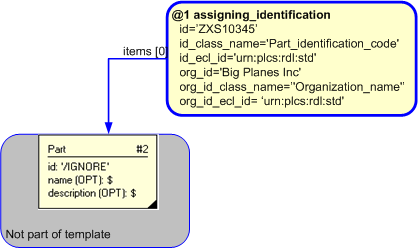
The instantiation diagram below shows the use of Identification_assignment for assigning an identification string 'GSKT000100' to the target. The identification_item target selected in this case is the entity "Part".
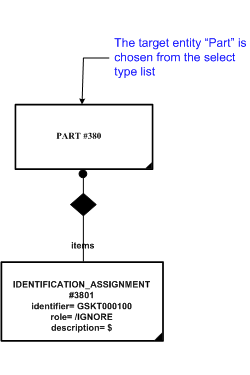
NOTE In EXPRESS, the select type is not instantiated.
The role and description attributes should be ignored. The section below describes how to represent reference data for the usage (role) of the identifier. The description of the identifier is provided through the reference data and its description in the reference data library.
Specifying the usage of the Identifier
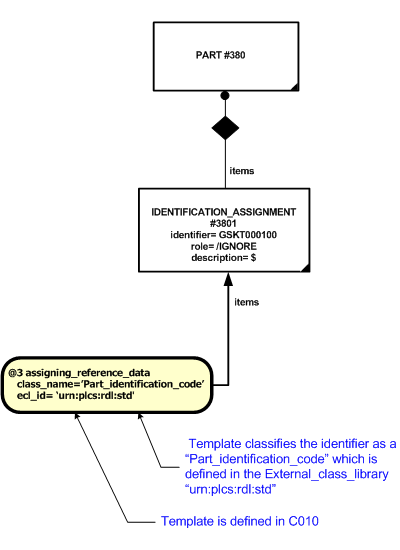
The usage of the identifier shall be specified. For example, whether the identifier is being used as a Serial Number, CAGE Code etc., depending upon what is being identified. This is provided through a Classification_assignment of the Identification_assignment instance. Typical values for the classification of identifiers are provided in the PLCS reference data library but should be a type of "Identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Identification code) (see the section on reference data at the end). The assignment of the clasification should be done in accordance with the capability C010: assigning_reference_data.
If a particular codification system has been used to make the identifier employed explicit, then that should be reflected in the type of identification code chosen. For example, if a part number has been encoded according to a specific coding standard, then there should be a class representing that standard as a subclass of "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code). The description of the class should make it clear which codification system and rules have been used.
The instantiated template diagram below shows the use of the assigning_reference_data template to apply a classification to the identification assignment object. In this example, the identifier is being classified as a type of "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) as defined within an external library ‘urn:plcs:rdl:std'.
NOTE An explanation of a template is provided in the Template overview section.
NOTE The "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) is a type of "Identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Identification code) as defined within the library specified.
NOTE The description of the "Part identification code" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part identification code) defined within the library specified, constrains the use of this reference data to instances of "Part".
Assigning the owner of the identifier
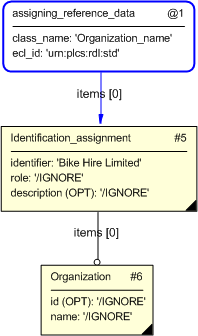
The organization or person that owns the identifier needs to be assigned to the identification through an instance of Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment. This associates an organization or person in an organization with the identifier of the target (in this case a Part). To indicate that the organization is the owner of the identifier, a separate Classification_assignment instance shall be provided where the value of the External_class name attribute, shall be "Owner of" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Owner of). In the example below, the identity ("Gasket Supply LLC") of the organization is provided through another instance of identification assignment which is then classified as an "Organization name" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Organization name) (as defined in the library at 'urn:plcs:rdl:std').
The assigning_organization template is used to provide this functionality which is documented within the Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment capability.
The Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment capability makes reference to the assigning_identification_with_no_organization template which is the second template defined within this capability and is designed to assign identifiers to objects which do not require a further Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment for their identification purposes.
This combination of associating an Identification_assignment to the product and subsequent assignments for usage and owner provides the equivalent of a Part Master Identification as described by the PDM Schema.
This section specifies how the information model can be further characterized by the assignment of additional information such as dates, approvals and people or organizations.
The following characterizations may apply.
Assignment of a date and/or time is described within capability C036: assigning_date_time.
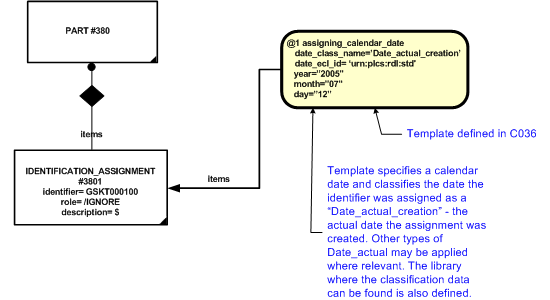
To provide an unambiguous reference to the identifier concerned, the date and/or time when the identifier was created should be provided. This should be represented using an instance of Date_or_date_time_assignment to link a Calendar_date or Date_time entity to the instance of Identification_assignment . This provides a date or date and time of when the assignment took place. The example below focuses on the template for assigning a Calendar_date .
The instance of Date_or_date_time_assignment should also be classified through another Classification_assignment. The assigned_class is represented as an instance of External_class whose attribute name is set to a type of "Date actual" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date actual) defined by reference data. The assigning_calendar_date template is used to provide this functionality and is shown below using the "Date actual creation" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date actual creation) (a type of "Date actual" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date actual) reference data).
The templates used to represent the basic requirements of identification have been described above.
The figure below, shows the collection of templates used within the template for identification which is specified in the template section below.
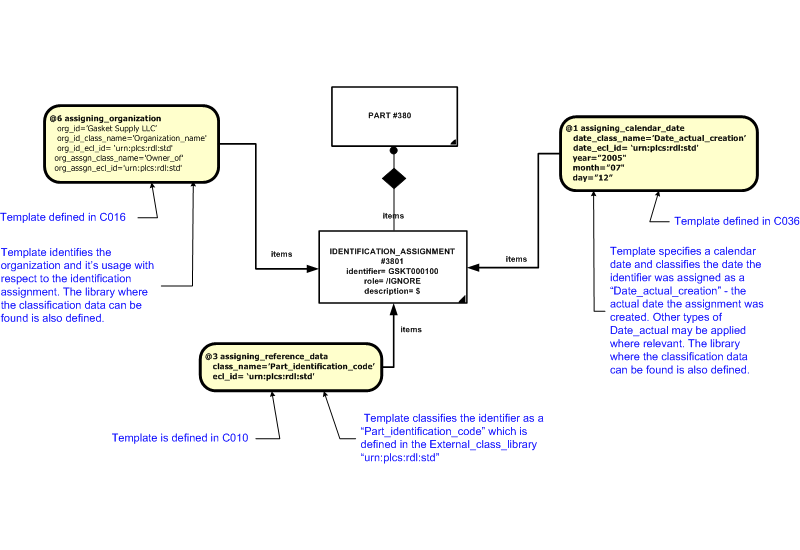
Since templates can be used in other templates, so the templates above can be used to form another; in this case, to represent the information needed for identification as a whole. The assigning_identification template presented below is defined with the capability template section later in this file. It's function is to gather the variable aspects of identification as well as to remove those parts mandated or to remove duplications. As the assignment of a date is optional, this is applied separately from the main template.
The figure below, shows the new template (assigning_identification) and how assigning_calendar_date should be used in conjunction for identification. Assigning_identification is specified in the capability template section.
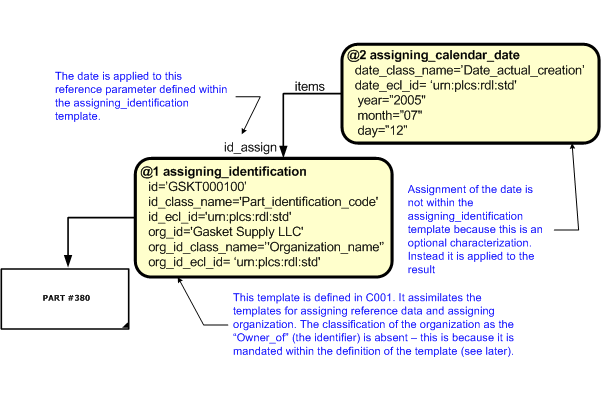
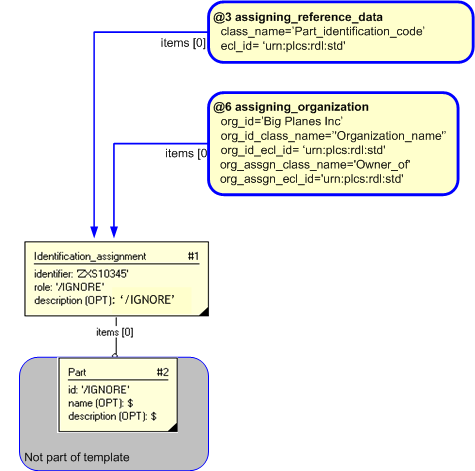
Having shown the mechanism for template instantiations in the previous section, we can expand this to provide a more complete example of what is instantiated.
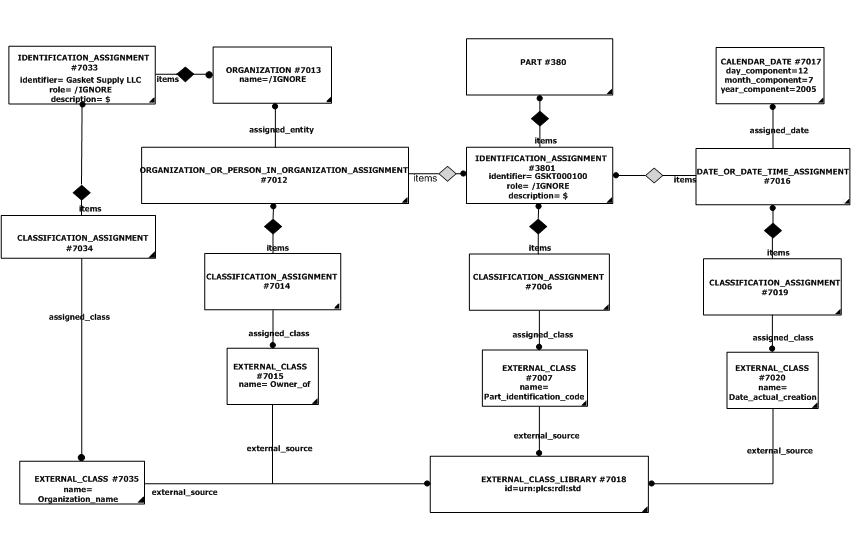
The instantiation diagram shows the use of three assignments to the identifier assigned to the Part entity, this provides a method for unique identification.
In general alias_identification should not be used. Multiple identification should be used to capture this information where term "alias" (or primary, secondary etc.,) is provided in an external_class through a classification_assignment to the identifier.
NOTE If one of the identifiers is to be "primary", then it should (in addition) be classified as such (using classification_assignment).
There is no restriction on the number of identification_assignments that can be associated with an item. Different organizations may refer to the same item with different identifiers. For example, the Prime Contractor may renumber parts provided by a supplier. Also, different types of identification may be applied to the same item. For example, in addition to the "Part Number" being assigned to a Part, a "Catalogue Number" may also be assigned.
NOTE There should only ever be one instance used to represent an organization in an exchange file.
Identifications from Different Organizations
The template instantiation diagram below shows how different organizations may refer to the same item with similar types of identifiers. In this case two organizations have assigned different identifiers to the same part, on different dates. This occurs in industry, where a part provided by a supplier is given a new part number by the assembly manufacturer.
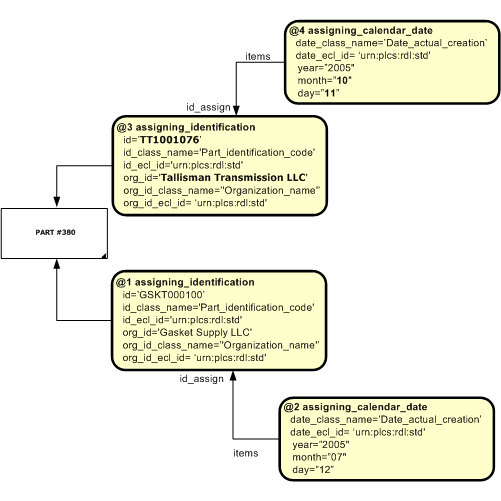
NOTE The two organizations are different, as are the identifiers, but the type of identifiers are the same.
The expanded instantiation diagram below shows how the templates can be expanded to the normal instantiation diagram.
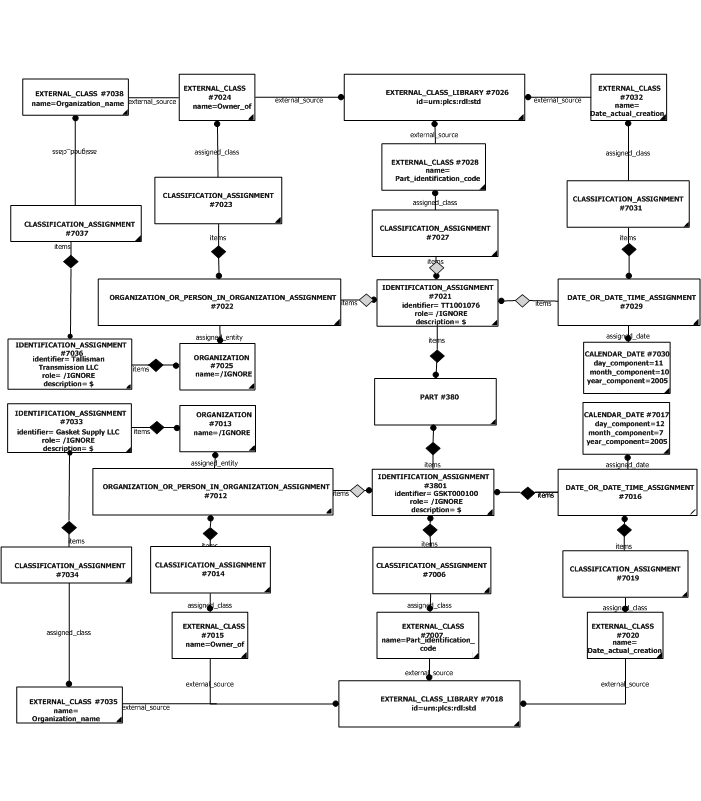
Different Types of Identification
The template diagram shows how different types of identification may refer to the same item.
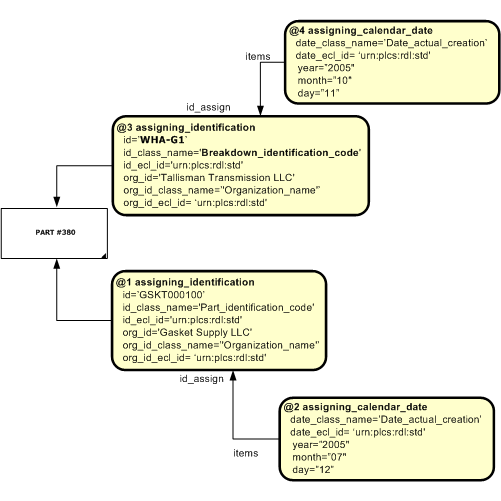
NOTE There are two types of identifier assigned to the same part in the example above. The identifiers are classified differently - according to their use; one as a part identification code, the other as a breakdown identification code. The organizations are different in the example, but the same organization may also issue more than one type of identifier for a part. The dates assigned are different, but they could also be identical - in that two different identifiers can be assigned on the same day.
The instantiation diagram below shows the expansion of the templates used.
While references to the PLCS standard reference data library (e.g. urn:plcs:rdl:std) have been used in the examples, for non-standard PLCS reference data developed by industry and organizations, such as the UK MoD, the URN will be a variation of the same theme (e.g. urn:plcs:rdl:ukmod).
The following sections define a set of templates for the capability, where a template is a specification of a set of entities that need to be instantiated to represent a given set of information.
This section specifies the template assigning_identification.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
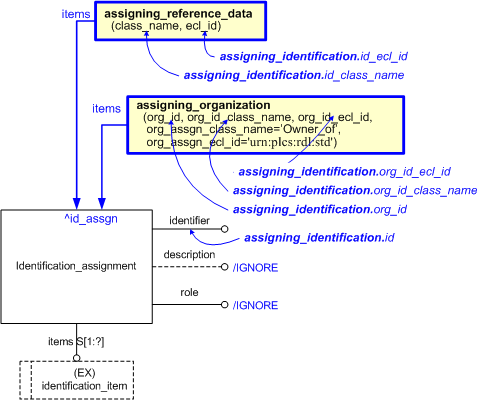
target
is the parameter to which the
Identification_assignment
is bound.
-- The template assigning_identification has an external reference
-- id_assgn. Bind this to the local external reference
-- id_assignment. It can now be the target for assigned dates
%^id_assgn = $assigning_identification.id_assgn%
-- assign date to identification_assignment in the role of "created"
/assigning_calendar_date(items=^id_assgn,
date_class_name='Date_actual',
date_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std',
year=@creation_year,
month=@creation_month,
day=@creation_day)/
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Identification_assignment.identifier | @id | — |
| Identification_assignment.role | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Identification_assignment.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
NOTE this characterization is optional.
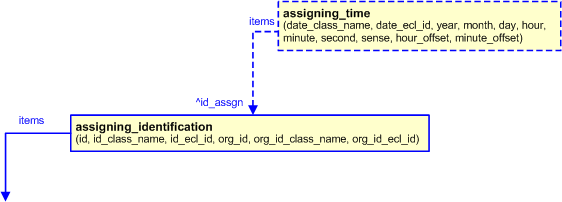
Times and dates can be associated with the assignment of an identifier by using the template assigning_time. For example, the time and date on which an identifier was created is represented by assigning a time to the Identification_assignment.
The model for assigning a time (and/or date) to an identifier is shown below.
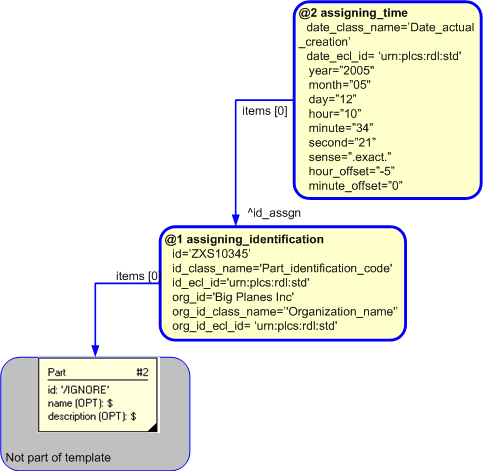
An example showing the assignment of a creation time (and/or date) to an identifier is shown below.
The instantiated templates for assigning a identification to a part is:
The instantiated templates for assigning a time (and/or date) to an identification
is shown below. Note the use of the reference parameter
$assigning_identification.id_assgn to identify the
Identification_assignment
instantiated by the template assigning_identification.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
An additional representation of an organization can be associated with the assignment of an identifier by using the template assigning_organization. For example, to specifiy both the Organization name AND an NCAGE of the Organization that is responsible for an identifier can be represented by associating an instance of the assigning_organization template to the Identification_assignment entity that is referenceable from the assigning_identification template.
The model for assigning an additional organization to an identifier is shown below.
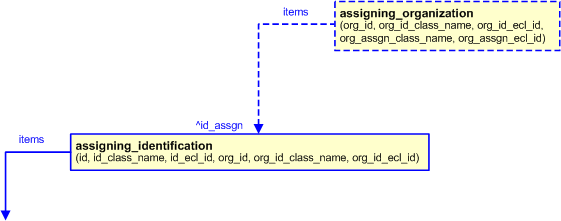
An example showing the assignment of an additional organization to an identifier is shown below.
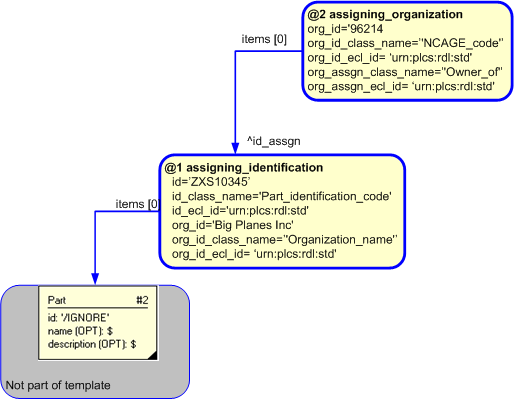
The instantiated templates for assigning a identification to a part is:
The instantiated templates for assigning an additional representation of the organization to an identification
are shown below. Note the use of the reference parameter
$assigning_identification.id_assgn to identify the
Identification_assignment
instantiated by the template assigning_identification.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
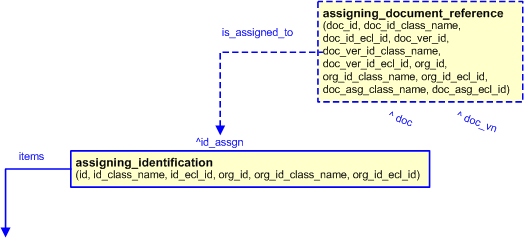
A document reference can be associated with the assignment of an identifier by using the template assigning_document_reference. For example, to reference the documented procedure or specification that is used in creating an identifier can be represented by associating an instance of the assigning_document_reference template to the Identification_assignment entity that is referenceable from the assigning_identification template.
The model for assigning an document reference to an identifier is shown below.
An example showing the assignment of a document reference to an identifier is shown below.
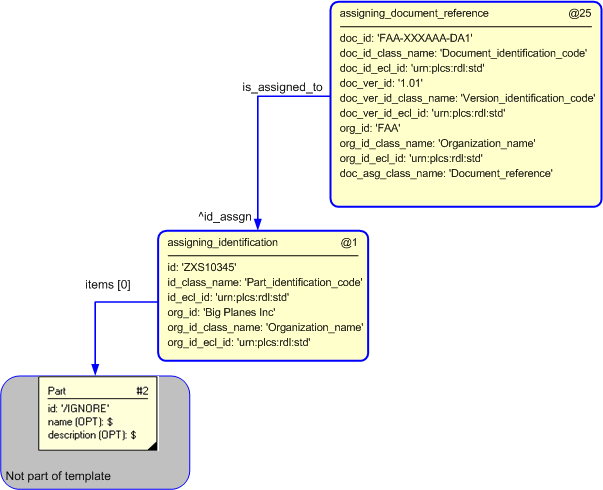
The instantiated templates for assigning a identification to a part is:
The instantiated templates for assigning a document reference to an identification
are shown below. Note the use of the reference parameter
$assigning_identification.id_assgn to identify the
Identification_assignment
instantiated by the template assigning_identification.
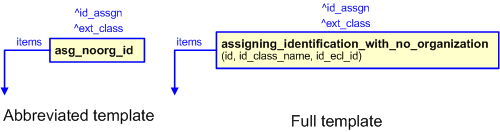
This section specifies the template assigning_identification_with_no_organization.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
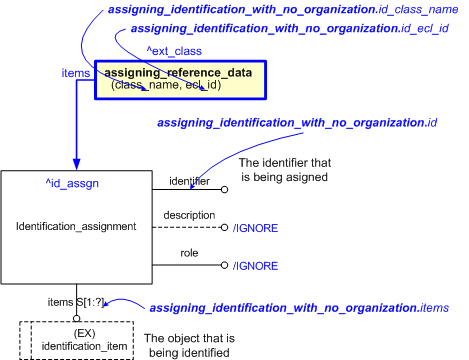
target
is the parameter to which the
Identification_assignment
is bound.
target
is the parameter to which the
External_class
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Identification_assignment.identifier | @id | — |
| Identification_assignment.role | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Identification_assignment.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
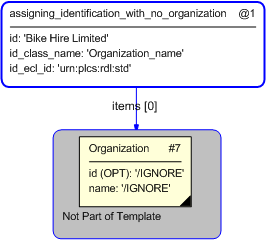
This capability "Identification" is dependent on the following capabilities:
The approach adopted here is compatible with that provided in the DOD Memorandum "The Department of Defence Guide to Uniquely Identifying Items, Version 1.3" dated November 25th, 2003.
A unique identifier is a set of data for tangible assets that is globally unique and unambiguous, ensures data integrity and data quality throughout life, and supports multi-faceted business applications and users. There are two key considerations in the unique identification of tangible items.
The first is enterprise identification. An enterprise is the entity responsible for assigning the unique identifier to a tangible asset. Enterprise means a business organization or firm, which is defined as a commercial partnership of two or more persons . For purposes of unique identification, an enterprise identifier will define each business location that has its own unique, separate and distinct operation. An enterprise identifier is a code uniquely assigned to an enterprise by a registration (or controlling) authority. A registration (or controlling) authority is an organization responsible for assigning a non-repeatable identifier to an enterprise [i.e., Dun and Bradstreet’s Data Universal Numbering System (DUNS) Number, Uniform Code Council (UCC)/EAN International (EAN) Company Prefix, or Defense Logistics Information Service (DLIS) Commercial and Government Entity (CAGE) Number].
Unique Identification of Items
The other key aspect of UID is the unique identification of each item that the enterprise produces. Unique identification depends upon a combination of data elements, which is determined by how the enterprise serializes tangible items. There are two acceptable methods of serialization – (1) Serialization within the enterprise, and (2) Serialization within the part number. Serialization within the enterprise occurs when each tangible item produced is assigned a serial number that is unique among all the tangible items produced by the enterprise and is never used again. The enterprise is responsible for guaranteeing unique serialization within the enterprise. Serialization within the part number occurs when each tangible item of a particular part number is assigned a unique serial number within that part number assignment. The enterprise is responsible for guaranteeing unique serialization within the part number.
NOTE The format of the identifier is not prescribed in this capability.
The figure below shows a classification of types of identifiers that might be used in association with an Identification_assignment.
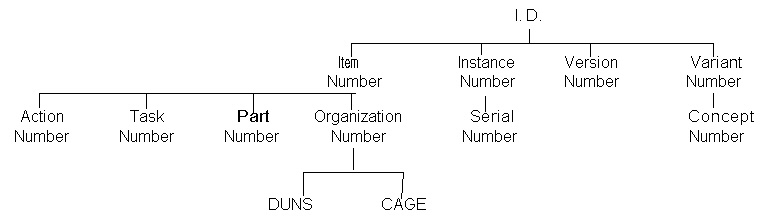
PLCS provides a generalized approach towards identification. All identifiers are represented similarly using Identification_assignment. On the other hand, PDM Schema uses the mapping of a significant identifier to the id attribute of the relevant entity (for example, Product) with Alias_identification being used for all other identifiers. Given an existing PDM Schema file, the Product.id attribute should be mapped to the Identification_assignment.identifier. Alias_identification instances should be mapped in the same way (may provide multiple identification).
Given a PLCS file, the Identification_assignment.identifier of the Part/Product should be mapped to the Product.id attribute when translating into a PDM Schema file. All other identification assignments in the PLCS system should be mapped to instances of alias identification.
NOTE The use of "Id_date" has been replaced with an "effectivity" of a date; specifically "Start" and "End" as possible classification data at the UK ISO meeting.
The following classes of reference data are required for this capability:
© OASIS 2010 — All rights reserved